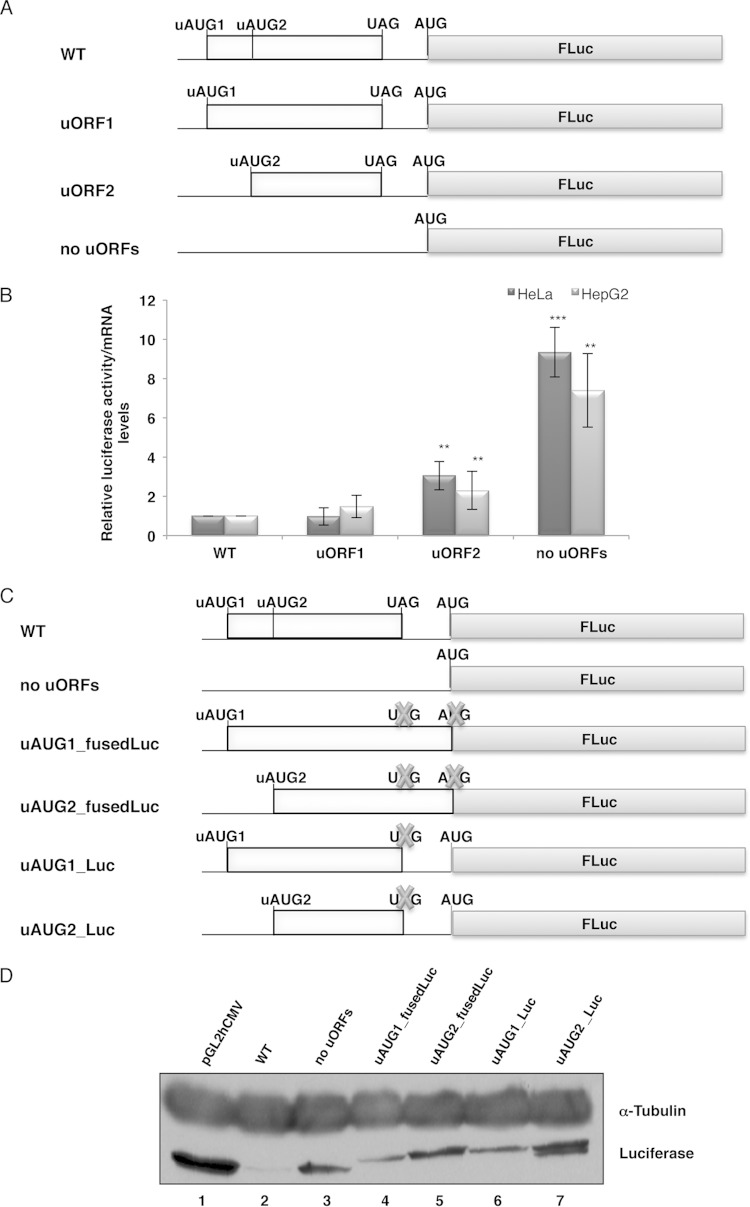
FIG 1.
The human HJV mRNA uORFs decrease the translational efficiency of the downstream main reporter ORF. (A) Schematic representation of reporter constructs. The human HJV 5′ UTR, encompassing the uORFs (light gray boxes) with intact initiation (uAUG) and termination (UAG) codons, was cloned into the empty vector (pGL2hCMV) upstream of the firefly luciferase gene coding region (FLuc) to create the wild-type construct (WT). The uAUGs were mutated individually (uORF1 and uORF2) or simultaneously (no uORFs). (B) The HJV 5′ UTR represses the activity of the downstream reporter coding sequence. HeLa and HepG2 cells were transiently cotransfected with each of the constructs shown in panel A and with the pRL-TK plasmid, encoding Renilla luciferase (RLuc). Cells were lysed 24 h later, and luciferase (Luc) activities and mRNA levels were measured by luminometry assays and RT-qPCR, respectively. The graph represents the data as translational efficiencies (relative luciferase activity/mRNA levels). Expression levels obtained from the WT construct were defined as 1. Average values and standard deviations for three independent experiments are shown. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t test (unpaired, two-tailed). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (C) Schematic representation of the constructs used for translation analysis. The WT and “no uORFs” constructs are the same as in panel A. The stop codon of each of the HJV uORFs was mutated in the uORF1 and uORF2 constructs, and each uORF was fused in frame with the downstream FLuc coding sequence, with (uAUG1_fusedLuc and uAUG2_fusedLuc) or without (uAUG1_Luc and uAUG2_Luc) mutation of the FLuc initiation (AUG) codon. Crosses represent the point mutations of the uORF stop codon and the FLuc initiation codon. (D) Translation initiation occurs at the HJV uORFs. Representative Western blot analyses show HeLa cell extracts transiently transfected with the constructs specified above the lanes. Immunoblotting was performed using an antiluciferase antibody to verify protein expression, and a human α-tubulin-specific antibody was used to control for variations in protein loading.