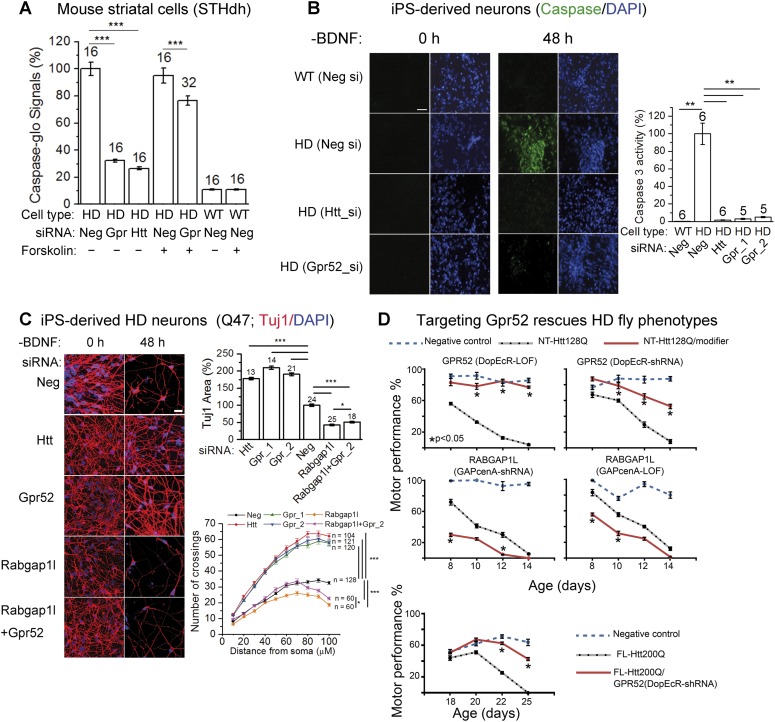
Figure 5. Lowering Gpr52 rescues human HD neurons and the in vivo fly HD models.
(A) Caspase-glo of STHdhQ7/Q111 (HD) or STHdhQ7/Q7 cells (WT) with indicated transfections (Neg: the non-targeting controls siRNA; Gpr: the Gpr52 siRNA smartpool; Htt: the Htt siRNA Hdh5) and compound treatments; statistical analyses by the two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-test. (B) Caspase 3 activity of patient iPS-derived neurons (Q47) measured by the fluorescent indicator dye before and after BDNF removal (scale bar: 200 µm). Bar plots: quantification of caspase 3 signals corrected by the total cell number (by DAPI) and normalized to the HD controls (second bar). Statistical analyses were performed by the two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-test. (C) Immunostaining of Tuj1 and DAPI showing loss of neurons of HD patient iPS-derived neurons (Q47) cultured under the BDNF-deprived condition with indicated transfections, and the rescue by knocking-down Htt or Gpr52 or Rabgap1l or Rabgap1l + Gpr52 (scale bar: 200 µm). Bar plots: quantification of the area in each field covered by the Tuj1 signal (Tuj1 area) and the nuclei counts. All data normalized to the non-targeting siRNA transfected control samples. Statistical analyses were performed by the two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-test. Sholl plots: the sholl analysis (Sholl, 1953) results plotted for each sample, ‘n’ indicated the number of analyzed neurons. Statistical analysis performed by two-way ANOVA tests. (D) Age-dependent motor performance in normal flies expressing elav-GAL4 driver alone (Negative control, blue dotted lines), HD flies expressing elav-GAL4 driven NT-Htt128Q or FL-Htt200Q alone (black dotted lines), or HD flies crossed to loss of function mutation (LOF) or knock-down (shRNA) lines of Drosophila homologs of Gpr52 or Rabgap1l (red lines). Lowering Gpr52 rescues the motor behavior deficits, whereas lowering Rabgap1l enhances the phenotype. n = 15, statistical analysis performed by one way ANOVA and Dunnett's post-tests.