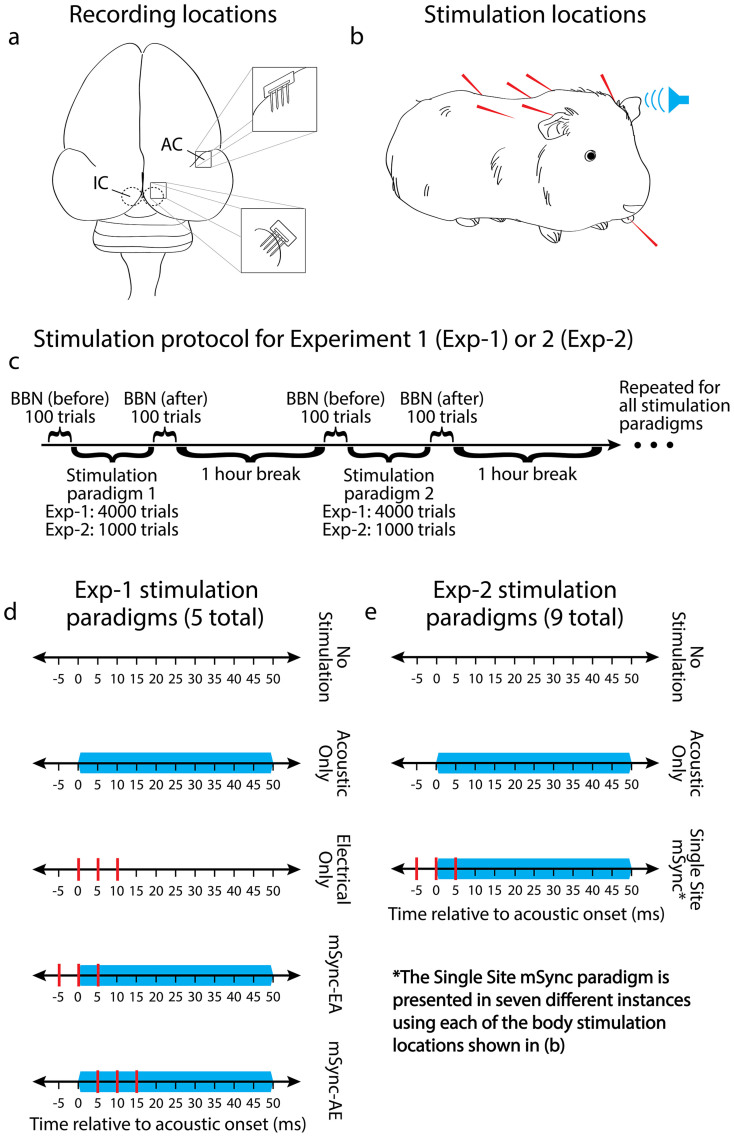
Figure 1. Experimental protocol.
(a) Neural recordings were made with 32-site NeuroNexus arrays in the right inferior colliculus (IC; its central nucleus) and auditory cortex (AC; its primary area). (b) Broadband acoustic stimulation was presented via a speaker coupled to the animal's left ear canal, and somatosensory electrical stimulation was presented via subcutaneous needle electrodes placed onto or within the tongue, neck, left mastoid, and right mastoid for Experiment 1 and onto or within the tongue, neck, left mastoid, right mastoid, left shoulder, right shoulder, and back for Experiment 2. (c) The stimulation protocol for Experiments 1 and 2 consisted of comparing the neural activity within the IC and AC in response to 100 trials of 70 dB SPL broadband noise (BBN) presented before and after a given stimulation paradigm, which are shown in (d) and (e) for Experiments 1 and 2, respectively. The stimulation paradigm order was randomized across animals with a one hour break between paradigms to reduce cumulative effects. (d) Single trials (inter-trial interval of 500 ms) are shown for the control (top three) and experimental (bottom two) paradigms used in Experiment 1. The blue bars represent a 50 ms duration (0.5 ms rise/fall time), 50 dB SPL BBN presented to the animal's left ear and the red lines are electrical stimulation pulses presented to the different body locations. Analysis was performed on 100 trials of acoustic-driven activity in response to 70 dB BBN recorded before and after 4,000 consecutive trials of each paradigm. For the Electrical Only, mSync-EA, and mSync-AE paradigms, each body location was stimulated for 1,000 trials in a randomized order across the four body locations for a total of 4,000 trials. (e) Single trials are shown for the control (top two) and experimental (bottom, Single Site mSync) paradigms used in Experiment 2. Each paradigm consisted of 1,000 consecutive trials of stimulation. Note that Single Site mSync is the same as mSync-EA from Experiment 1 except it consisted of only one body site at a time for all 1,000 trials. The seven different body locations shown in (b) were used, resulting in seven different experimental paradigms.