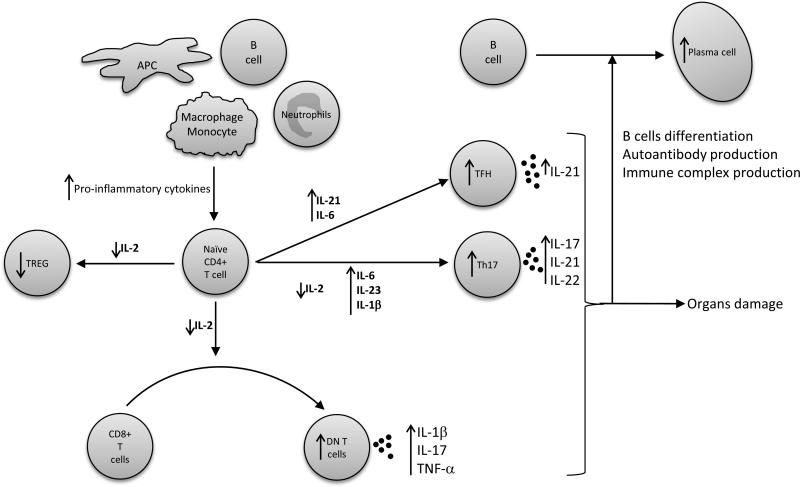
Figure 2. T cells differentiation and cytokines aberration in SLE patients.
The cytokines produced by macrophages, antigen-presenting cells (APC), B cells, neutrophils and activated T cells, along with the decreased IL-2, influence the development of naïve CD4+ T cells in SLE patients. These alterations favor the development of Th17, TCRab+CD4-CD8 double negative (DN) and T follicular helper (TFH) T cells, whilst inhibiting regulatory T cells (TREG) differentiation. Collectively, these abnormalities enhance B cell maturation and differentiation, antibody production and immune complex formation, and also promote organ damage. Arrows indicate increased/decreased cytokines or cell subset in SLE compared to control.