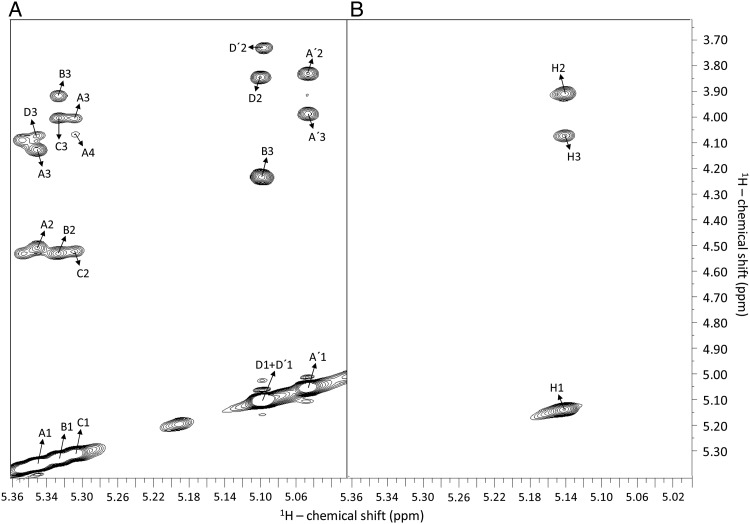
Fig. 5.
1H–1H NOESY spectra of oligosaccharides from sulfated fucans Structures 1 (A) and 2 (B), recorded with mixing time at 250 ms and temperature at 298 K. (A) Octasaccharide Lv I obtained from SEC fractionation (Figure 2) after the 6 h-mild acid hydrolysis with 0.01 M HCl at 60°C. The fucosyl units with different sulfation patterns are labeled as follows: A for 2-sulfation, B for 2,4-disulfation, C for 2-sulfation, D for 4-sulfation, A′ for 2-desulfation (non-sulfation) and D′ for the non-reducing end 4-sulfated unit. The numbers after these letters indicate the respective hydrogens within the sugar chain. Inter-residual NOE signals are always assigned between the anomeric 1H1 and the 1H3 of the subsequent unit. They necessarily correspond to the glycosidic bonds. Intra-residual NOE are always between the anomeric 1H1 and 1H2, or 1H3 for the single case of the disulfated unit labeled as B. (B) Oligosaccharides obtained by the 2 h-mild acid hydrolysis with 0.04 M HCl at 60°C (Supplementary data, Figure S3). Note that there are just two types of NOE connectivities for the oligosaccharides from sulfated fucan Structure 2: the inter-residual NOE between the anomeric 1H1 and 1H3, which represents the glycosidic bonds, and the intra-residual NOE between the anomeric 1H1 and the 1H2. The spectra were recorded at a Bruker 600 MHz instrument.