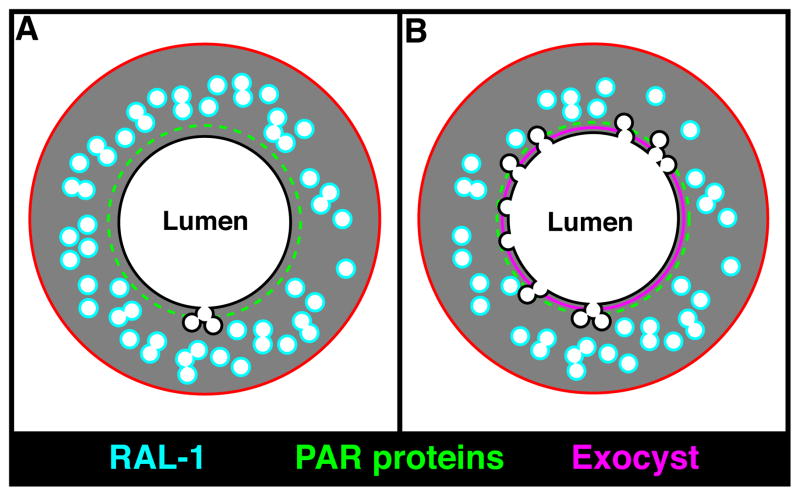
Figure 8. Model for excretory canal lumen formation.
(A) Schematic of the excretory canal shown in transverse section, with the PAR proteins (green) and RAL-1 (cyan) present at distinct but overlapping domains. (B) At regions containing both PAR proteins and active RAL-1, the exocyst (magenta) is recruited and triggers the docking and fusion of canalicular vesicles with the lumenal surface, leading to canal expansion and increased exchange of water and salt.