Fig 1.
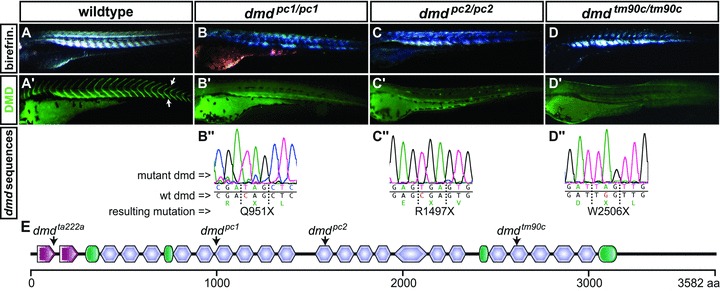
Novel dmd mutants identified in a non-complementation screen. (A) Birefringence of the muscle of a 3 dpf WT larva, evoked by polarized light, indicates an ordered array of myofilaments. (B–D) All novel dmd mutants display reduced muscle birefringence. (A’) Immunofluorescence revealed that dystrophin (green) is present at the somite borders (arrows) in siblings, (B’–D’) but absent in the homozygous dmd mutants. (B”–D”) Genomic sequencing of the dmd mutants revealed premature stop codons within exon 21 of dmdpc1/pc1, exon 32 of dmdpc2/pc2 and exon 53 of dmdtm90c/tm90c. (E) Arrows in the schematic diagram of zebrafish dystrophin point to the location of the premature stop codon encoded in each indicated mutant. Amino acid positions are displayed in the scale bar below; calponin-homology domains are in red, hinge domains in green and spectrin-like repeats in blue.
