Fig 7.
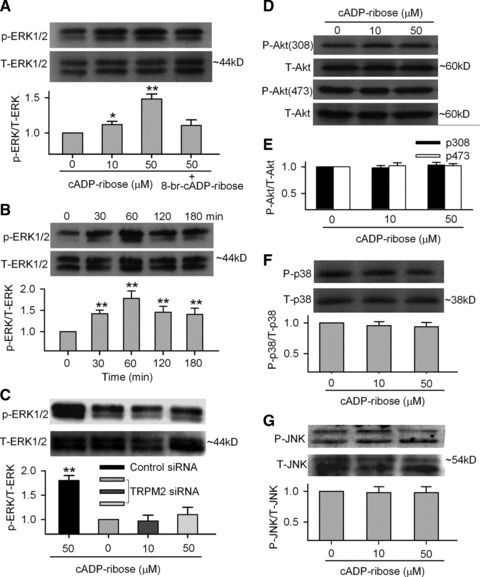
Cyclic ADP ribose and proliferation-related kinases. (A) ERK1/2 phosphorylation at Thr185/Tyr187 was enhanced in the presence of cADPR (10 and 50 μM) for 60 min. and 8-Br-cADPR (100 μM) reduced the effect (upper panels). Mean values (lower panel) for ratio of p-ERK1/2:total ERK1/2 (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus 0 μM cADPR). (B) Time-dependent effect of cADPR on ERK1/2 phosphorylation and mean values for ratio of p-ERK1/2:total ERK1/2 in the presence of cADPR for 30, 60, 120 and 180 min. (n = 3, **P < 0.01 versus 0 μM cADPR). (C) ERK1/2 phosphorylation and mean values for ratio of p-ERK1/2:total ERK1/2 in the presence of cADPR in the cells transfected with control siRNA or TRPM2 siRNA for 72 hrs (n = 3, **P < 0.01 versus 0 μM cADPR). (D) Akt1 phosphorylation at Thr308 and Ser473 was not affected by cADPR (10 and 50 μM for 60 min.). (E) Mean values for ratio of p-Akt(308):total Akt (n = 3) and p-Akt(473):total Akt (n = 3). (F) p38 MAPK phosphorylation levels at Thr180/Tyr182 were not changed when incubated with cADPR (10 and 50 μM) for 60 min. (n = 3). (G) JNK phosphorylation levels at Thr183/Tyr185 were not changed when incubated with cADPR (10 and 50 μM) for 60 min. (n = 3).
