Figure 3.
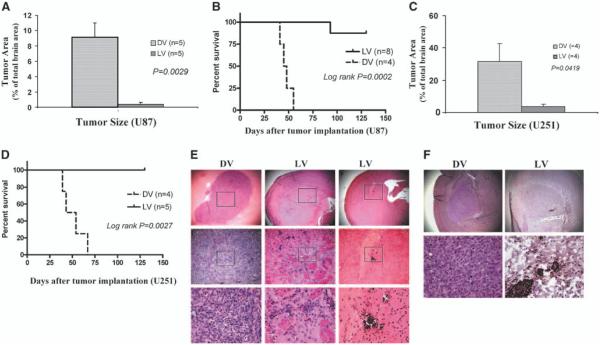
A single intratumoral administration of myxoma virus produced smaller tumors and prolonged survival in both U87 and U251 orthotopic human glioma animal models. U87 and U251 human glioma xenografts were established in brains of CD-1 nude mice. Twelve days after tumor implantation, animals were injected intratumorally with myxoma virus (5 × 106 PFUs/mouse) or dead myxoma virus (control). A, animals were sacrificed on day 35 and tumor size was measured. U87 tumors were significantly smaller in the live vMyxgfp–treated group than in the dead myxoma virus–treated group (tumors occupied 0.359% versus 9.16% of coronal sections of the brain, respectively; Mann-Whitney, P = 0.0029); most live vMyxgfp–treated animals had no visible microscopic tumors. B, live vMyxgfp–treated nude mice with orthotopic U87 xenografts survived significantly longer after a single administration of vMyxgfp (5 × 106 PFUs/mouse) delivered intratumorally. Live vMyxgfp–treated mice had a significantly longer survival (median survival not reached) than dead myxoma virus–treated animals (median survival, 47.3 days; log-rank, P = 0.0002). Only one of eight (12.5%) live vMyxgfp–treated animals died whereas all (100%) dead myxoma virus–treated animals died. The experiment was arbitrarily terminated on day 130. A similar result was found using the U251 orthotopic human glioma animal model. C, the U251 tumors were significantly smaller in the live vMyxgfp–treated group than in the dead myxoma virus–treated group (tumors occupied 3.77% versus 31.66% of coronal sections of the brain, respectively; Mann-Whitney, P = 0.0419). D, median survival was also significantly longer in the live vMyxgfp–treated (none of the animals died) than the dead myxoma virus–treated group (live vMyxgfp not reached versus 50.7 days; log-rank, P = 0.0027). E, histologic examination of the U87 orthotopic glioma model showed large tumors in the putamen of dead myxoma virus–treated mice (left column; top, ×25; bottom, ×400) but showed only microscopic residual tumor cells and focal calcification in live vMyxgfp–treated mice. Most live vMyxgfp–treated mice also had slightly dilated ventricles (middle and right columns; top, ×25; bottom, ×400). F, myxoma virus protein was detected within the microscopic residual U87 tumor cells in the brain of live vMyxgfp–treated animals (right column; top, ×25; bottom, ×400) 130 days after infections, but not in the dead myxoma virus–treated animals (left column; top, ×25; bottom, ×400).