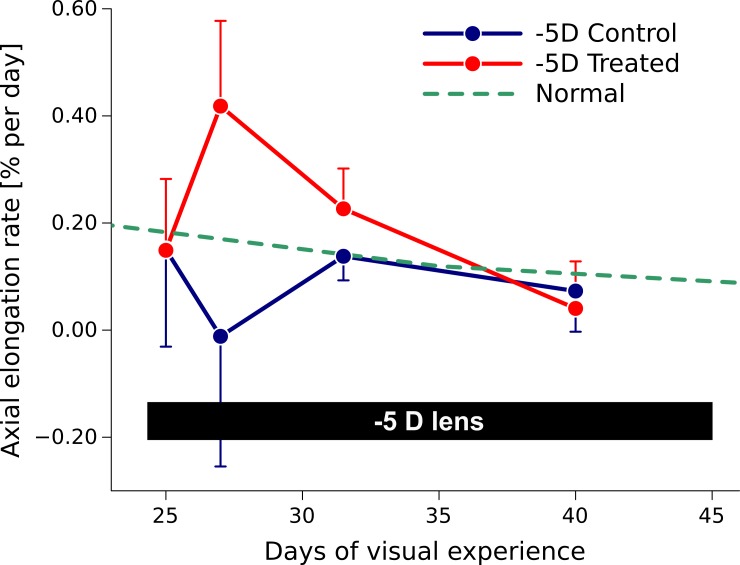
Figure 5.
Axial elongation rate in normal animals and animals in which one eye was treated with a −5 D lens (−5 D Treated) while the other eye was left as control (−5 D Control). The axial elongation rate increased rapidly in the treated eye, and then gradually decreased to normal values as the eye adapted to the −5 D lens (data reproduced from Siegwart and Norton23).