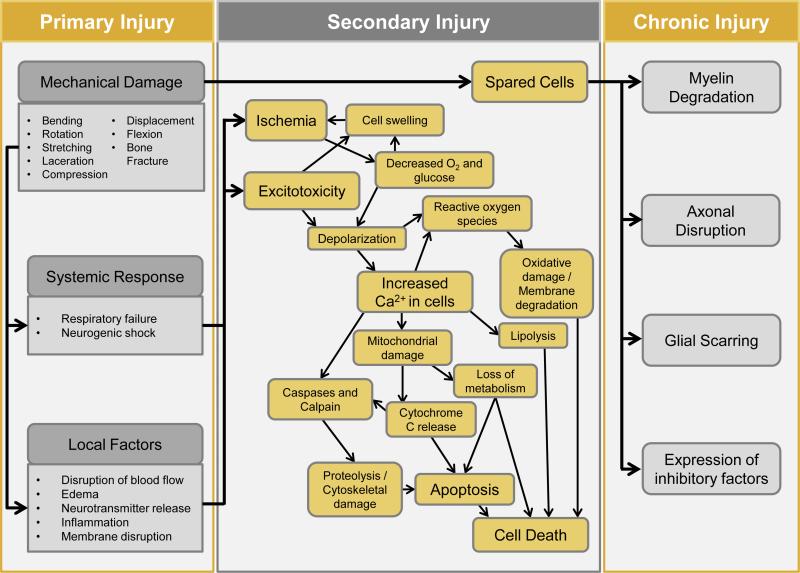
Figure 1.
Pathophysiology of spinal cord injury, demonstrating pathological events during primary SCI, secondary SCI, and recovery phases. Mechanical trauma leads to disruption in blood flow, hemorrhage, ischemia, hypoxia, membrane damage, edema, glutamate release, and inflammation. These are often followed by glutamate mediated cytotoxicity, calcium mediated injury, lipid peroxidation, electrolyte imbalance and apoptosis. Dysfunction during recovery resulting from injuries occurs because of neuron loss and an environment that inhibits regeneration.