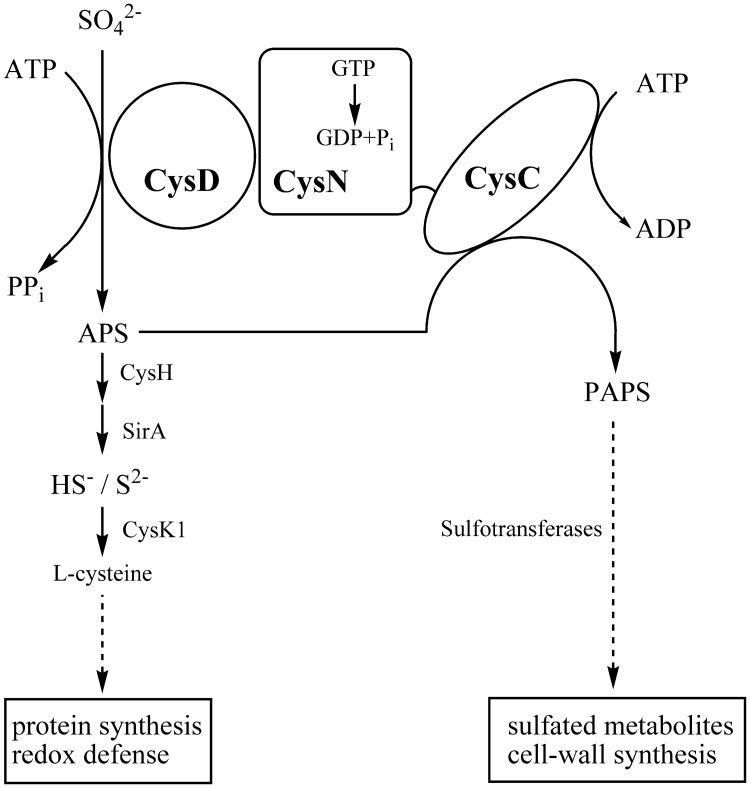
Fig 1. The sulfate activating complex in M. tuberculosis is an important branching point of sulfur assimilation.
The complex consists of two polypeptides, CysD (Rv1285) and CysN (Rv1286). The primary product APS is used in the reductive branch of the APS/PAPS pathway (to the left), which supplies reduced sulfur for the biosynthesis of cysteine. Phosphorylation of APS is catalyzed by the CysC domain of CysN. PAPS is utilized by sulfotransferases in the biosynthesis of sulfated metabolites (e.g. SL-1) contributing to cell wall synthesis and growth.