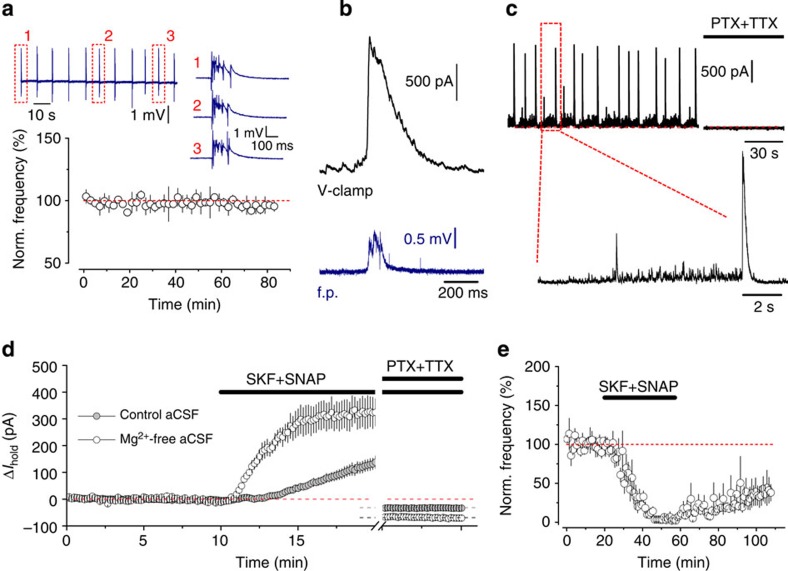
Figure 3. Synaptic GABA release during epileptiform activity.
(a) Regular stereotypic epileptiform discharges (average frequency: 0.15±0.05 Hz; n=3) induced in Mg2+-free aCSF. Insert: sample field potential recording traces. (b) An example of a large GABAAR-mediated current in a CA1 pyramidal neuron (black, whole-cell voltage clamp, Vhold=0 mV) associated with a field potential (f.p.) burst (blue). (c) Typical recording of GABAAR-mediated drive onto a pyramidal neuron (Vhold=0 mV) during epileptiform activity. PTX, picrotoxin; TTX, tetrodotoxin. (d) Time course of Ihold changes induced by co-application of SKF89976A and SNAP5114 in control and Mg2+-free aCSF (rate of Ihold increase calculated 1–5 min after GAT inhibitors application in 0 Mg2+: 1.1±0.2 pA s−1; in control: 0.16±0.04 pA s−1; n=4 for each condition; P=0.004, t-test). (e) GAT inhibitors suppress the frequency of epileptiform discharges (3.6±2.6% of baseline; n=4, P<0.001, paired t-test). Error bars, s.e.m.