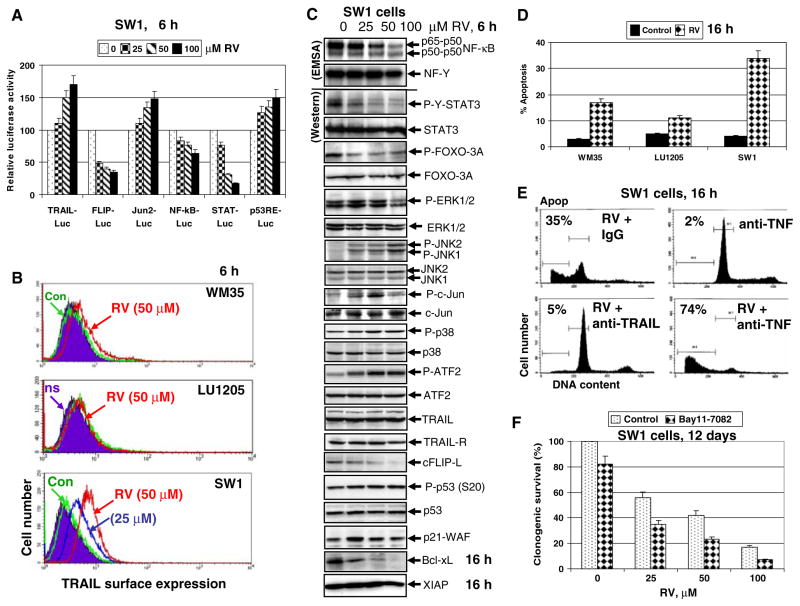
Fig. 6.
Effects of resveratrol (RV) on cellular proteins controlling cell survival and apoptosis in SW1 melanoma cells. (a) Effects of RV on NF-κB-, AP-1, STAT- and p53-dependent luciferase reporter activities, TRAIL and FLIP promoter activities. (b) Effects of RV on TRAIL surface expression in SW1 melanoma cells. Immunostaining with anti-TRAIL-PE mAb and FACS analysis were used. (c) Effects of RV (50 μM) on basal nuclear NF-κB and NF-Y activities in SW1 cells determined by EMSA 6 h after treatment. Positions of DNA-binding complexes are indicated. Free labeled probes are not shown. Western blot analysis was performed for detection of total and phosphoprotein levels of STAT3, FOXO-3A, ERK1/2, JNK1/2, cJun, p38MAPK, ATF2, TRAIL, TRAIL-R, cFLIP, phospho-p53 (Ser20), total p53 and p21-WAF 6 h after treatment with RV. Western blot analysis of Bcl-xL, XIAP and β-actin levels 16 h after treatment with RV. (d) Levels of apoptosis induced by RV (50 μM) in melanoma lines 16 h after treatment. (e) Effects of anti-TRAIL (5 μg/ml) and anti-TNF (5 μg/ml) inhibitory mAbs on RV-induced apoptosis in SW1 cells. PI staining DNA and flow cytometry analysis were used for cell cycle-apoptosis analysis. (f) Clonogenic survival assay for combined treatment of SW1 cells by RV (0–100 μM) and Bay 11-7082 (5 μM). Error bars represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments