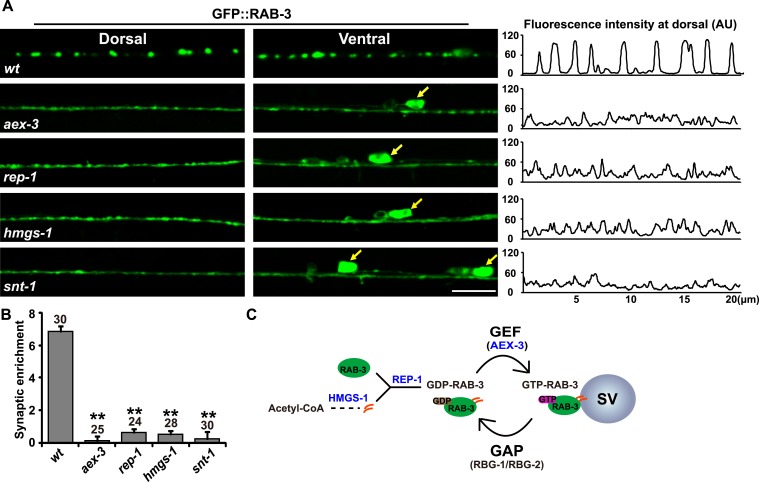
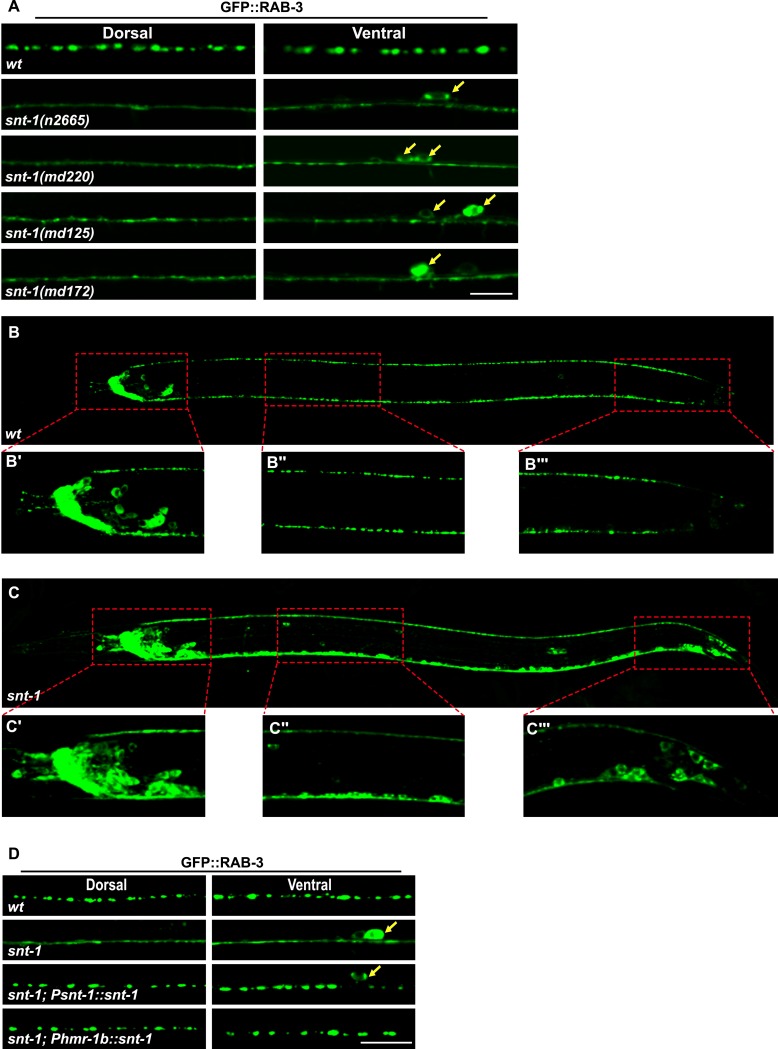
Figure 1. RAB-3 synaptic vesicle association requires SNT-1.
(A) Punctate distribution of GFP::RAB-3 in C. elegans motor neurons in wild-type animals (top). The GFP::RAB-3 puncta become diffuse in aex-3, rep-1, hmgs-1, and snt-1 mutants (lower panels). Yellow arrows indicate the cell bodies along the ventral cord. A representative line-scanning image for each genotype is shown in the right panel. (B) Quantification of the synaptic enrichment in wild-type, aex-3, rep-1, hmgs-1, and snt-1 animals. Data are presented as mean ± SD; **p < 0.01. (C) Schematic representation of the RAB-3/SV association and dissociation cycle. Scale bar, 5 µm.