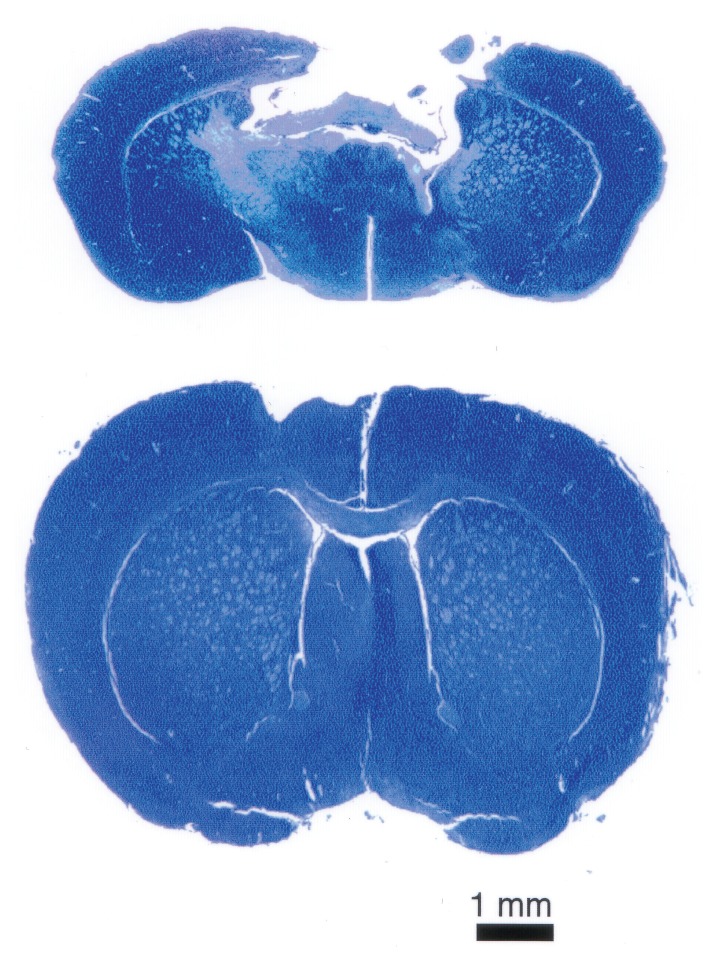
Figure 1.
EPO protects the brain from traumatic injury. Blunt trauma delivered to the left side of the cerebral cortex of a mouse produces a large cavitary lesion densely populated by inflammatory cells by 7–10 d after injury (top). Administration of EPO after injury (bottom) markedly reduces the size of the lesion. Few inflammatory cells can be found within and surrounding the area of damage. Image reproduced from (3) (copyright © 2000, The National Academy of Sciences).