Figure 3. Modulation of inflammatory processes by the UPR in chondrocytes in OA.
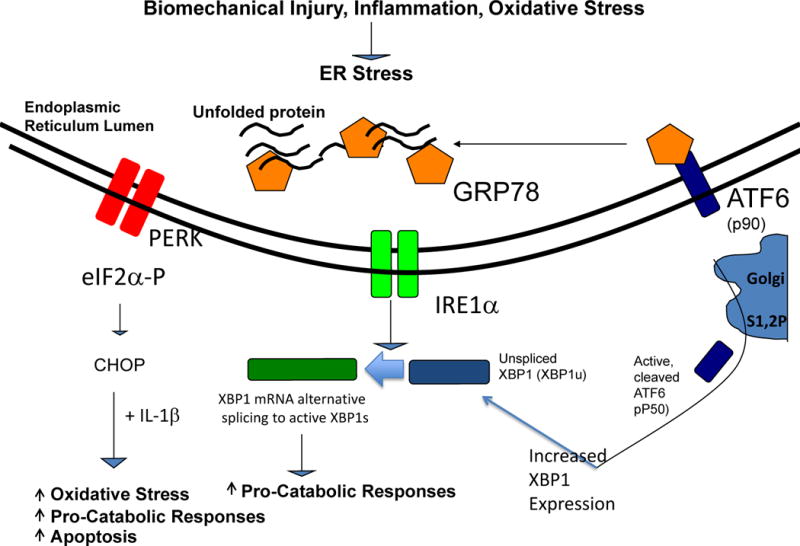
The UPR signalling cascades triggered by dissociation of the chaperone GRP78 from the ER transmembrane proteins PERK, IRE1, and ATF6, and activated by biomechanical injury, nitric oxide, and certain inflammatory mediators. Alternatively spliced, transcriptionally activated XBP1 (XBP1s) promotes chondrocyte maturation to procatabolic hypertrophic differentiation, mediated in part by cross-talk with the ATF6 pathway. XBP1s also drives matrix pro-catabolic responses in response to IL-1β, as does excess CHOP, another terminal UPR effector. CHOP also promotes chondrocyte superoxide production and apoptosis. Knock-out of CHOP is chondroprotective in mouse knee instability-induced OA in vivo.
Abbreviations: ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GRP78, 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein; IRE1, inositol-requiring protein 1; PERK, protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase; UPR, unfolded protein response; XBP1, X-box-binding protein 1; XBP1s, X-box-binding protein 1 splicing form.
