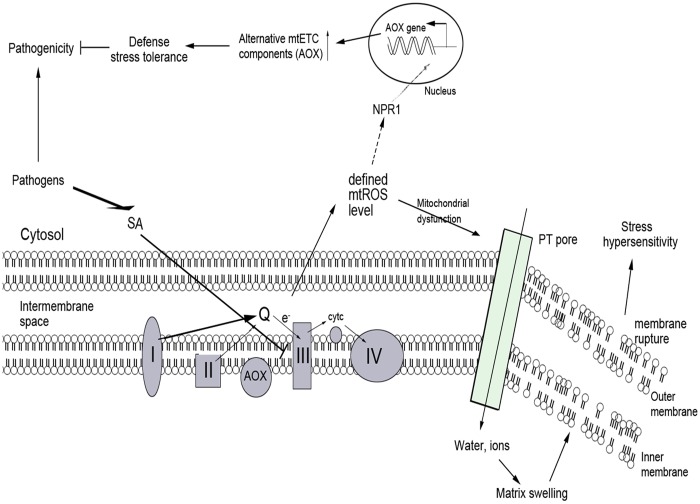
Fig 11. Hypothetical model for mitochondrial dysfunction and AOX defense in SA-induced ROS signal pathway.
SA blocks electron flow, and inhibits the function of mtETC components such as CYT pathway, resulting in increased mtROS. On one hand, mtROS causes mitochondrial dysfunction associated with morphology transition and depolarization of membrane potential. On the other, the expression of the unique alternative components of mtETC (AOX) appears to increase in response to discruptions in respiratory homeostasis, and further, AOX contributes to defense response to invading pathogens in whole plants.