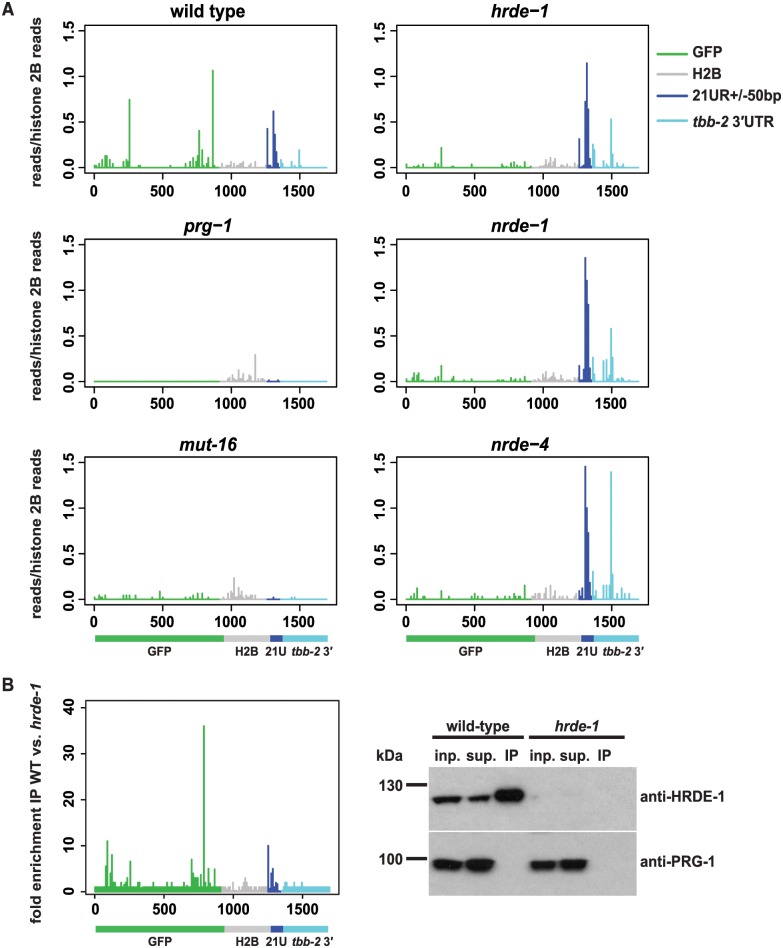
Fig 1. 22G-RNAs distal to piRNA target sites require the nuclear RNAi pathway.
A) Small RNA high-throughput sequencing reads with unique matches antisense to the piRNA sensor from wild type and various mutant animals as indicated. The values of the y-axes correspond to reads matching the piRNA sensor normalised to reads matching Histone 2B (his-58). The x-axes represent the relative position of reads in the piRNA sensor transgene with numbers representing nucleotides from the start codon (set as 0). The transgene structure is schematically represented at the bottom. Colour code: green = GFP, grey = Histone 2B (his-58), dark blue = 21UR-1 target site plus/minus 50 bp, light blue = tbb-2 3′UTR. B) Left panel: Enrichment of small RNA high-throughput sequencing reads with matches antisense to the piRNA sensor in HRDE-1 Immunoprecipitation (IP). Displayed is the fold enrichment of reads found in anti-HRDE-1 IP from wild type versus hrde-1 mutant animals. X-axis, schematic representation of the transgene and colour code as in A). Right panel: Western blot of anti-HRDE-1 Immunoprecipitation from wild type (left 3 lanes) and hrde-1 mutant (right 3 lanes) animals. Antibodies used for western blot are anti-HRDE-1 and anti-PRG-1 as loading control. Inp. = 1% input, sup. = supernatant, IP = Immuoprecipitate. On the left, the relative migration of the 130 and 100 kDa bands of the PAGE Ruler Plus (MBI Fermentas) marker are indicated.