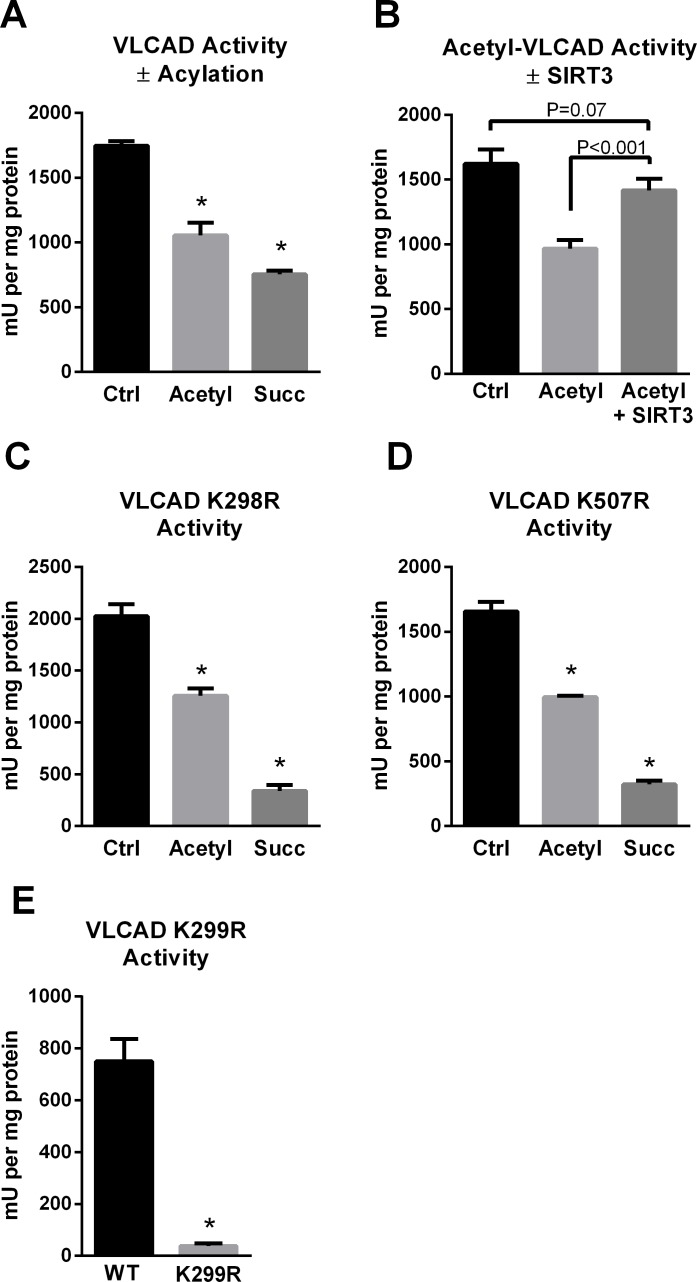
Fig 3. The SIRT3/SIRT5 target site K299 is critical for FAD binding and VLCAD activity.
A) Chemical acetylation and succinylation both reduce enzymatic activity of recombinant VLCAD. B) Incubation of acetylated VLCAD with SIRT3 rescues activity, while incubation of succinylated VLCAD with SIRT5 does not (not shown). C) Mutant K298R retains sensitivity to acylation-induced loss of activity,suggesting that K298 does not play a mechanistic role in the reduced activity. D) Likewise, mutant K507R retains sensitivity to acylation-induced loss of activity, suggesting that K507 also does not play a mechanistic role in the reduced activity. E) K299 is highly sensitive to conservative substitution with arginine. K299R lost the yellow color characteristic of FAD and consequently became inactive. All bar graphs depict means and standard deviations of triplicate assays. *P<0.01 versus wild-type or control.