Fig. 4.
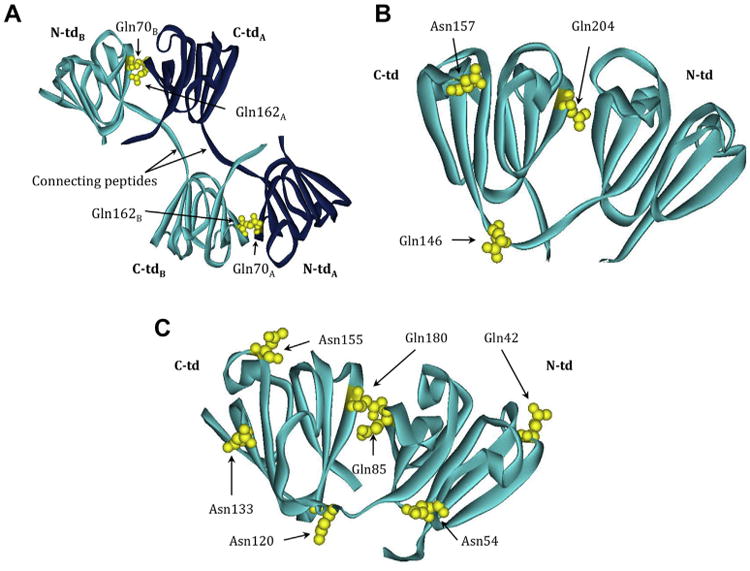
β-crystallin structures highlighting labile Asn/Gln that are deamidated in vivo. Ribbon model of (A) βB2 homodimer (PBD: 1YTQ) showing Gln70, Gln162, and Gln184. The light and dark blue color scheme represents the two homologous monomers. Ribbon model of (B) truncated (tr) βB1 homodimer (PBD:1OKI) showing Gln146, Gln157, and Gln204. Ribbon model of (C) βA4 monomer (PBD:3WLK) with residues homologous to Gln42, Asn54, Gln85, Asn120, Asn133, Asn155 and Gln180 found in βA3 highlighted. Dark blue, polypeptide chain A; light blue, polypeptide chain B; N- and C-td, N- and C-terminal domains. Deamidated residues shown in yellow. The numbering system is based on the amino acid sequence with the N-terminal methionine retained in βA3, but post-translationally removed in βB1 and βB2.
