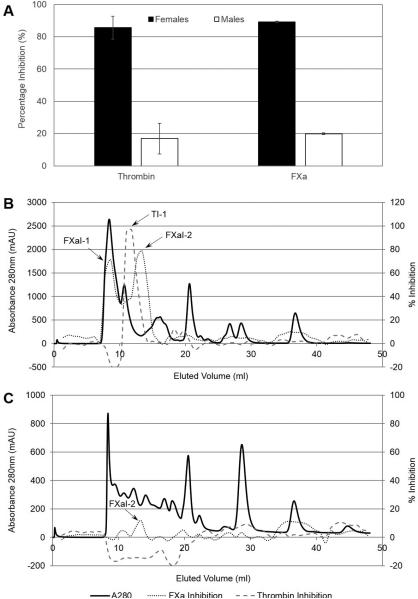
Figure 1. Anticoagulant activity of R. pulchellus salivary gland extracts.
(A) The amidolytic activities of thrombin and FXa were measured in the presence of 15 ug of female or male crude salivary gland extracts. Female extracts were able to inhibit both thrombin and FXa to higher than 80% while male extracts inhibited the enzymes lower than 20%. (B) Crude salivary gland extracts from female ticks were subjected to fractionation by size exclusion chromatography. (C) Crude salivary gland extracts from male ticks were subjected to fractionation by size exclusion chromatography. Fractions from (B) and (C) were tested for their ability to inhibit the amidolytic activity of FXa and thrombin. Female extracts inhibited FXa (FXaI-1 and FXaI-2) and thrombin (TI-1) while male extracts only inhibited FXa to a small extent (FXaI-2).