Fig 1. TR-FRET screen for RIN1::ABL1 interaction inhibitors.
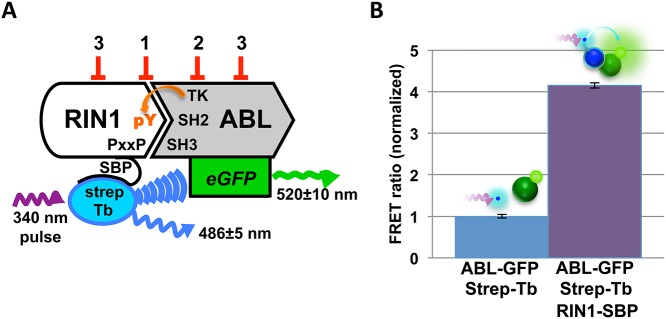
(A) Binding between RIN1 and ABL is initiated by a proline rich motif in RIN1 binding to the ABL-SH3 domain. ABL phosphorylates RIN1-Y36, which then binds the ABL-SH2 domain. For the assay, ABL was fused to eGFP and RIN1 was fused to a streptavidin binding peptide (SBP) that connects to a streptavidin-terbium complex. A 340 nm pulse excites terbium, which can transfer energy to excite the GFP acceptor if the fluorophores are in close proximity, reflecting RIN1::ABL binding. Predicted FRET inhibitor classes: 1. Orthosteric inhibitors, 2. Direct ABL kinase inhibitors and 3. Allosteric inhibitors. (B) RIN1::ABL binding was quantified as a FRET ratio: GFP emission at 520 nm to terbium emission at 486 nm. The negative control was donor and acceptor fluorophores only (no RIN1) and was normalized to 1.
