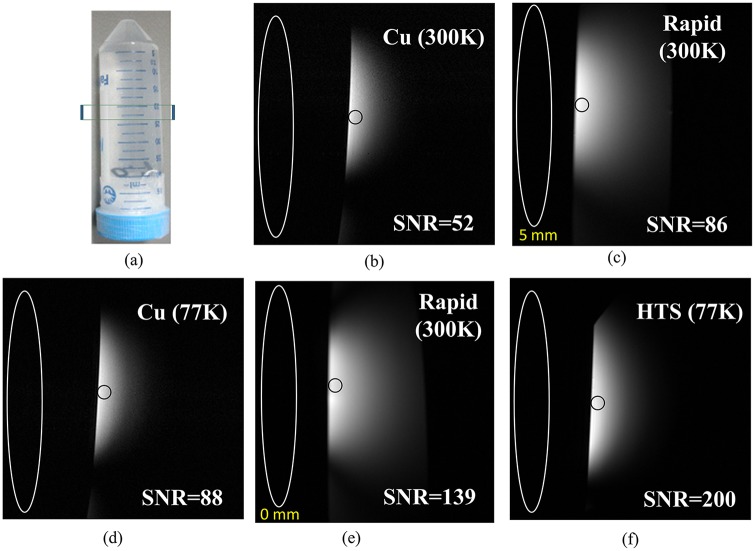
Fig 2. The imaging experiment of the phantom using the different coils.
(a) A picture of the cylindrical phantom filled with 0.5 S.m-1 NaCl solution. (b) The copper surface resonator at 300 K with SNR of 52. (c) The QD surface resonator at 300 K with the distance of 5 mm with SNR of 86. (d) The copper surface resonator at 77 K with SNR of 88. (e) The QD surface resonator at 300 K close to the phantom with SNR of 139. (f) The HTS surface resonator at 77 K with SNR of 200. The SNR gain is mainly contributed by the reducing noise. A SNR gain of 1.43 was obtained by using the HTS-based surface resonator with the same acquisition time as the QD surface resonator close to the phantom.