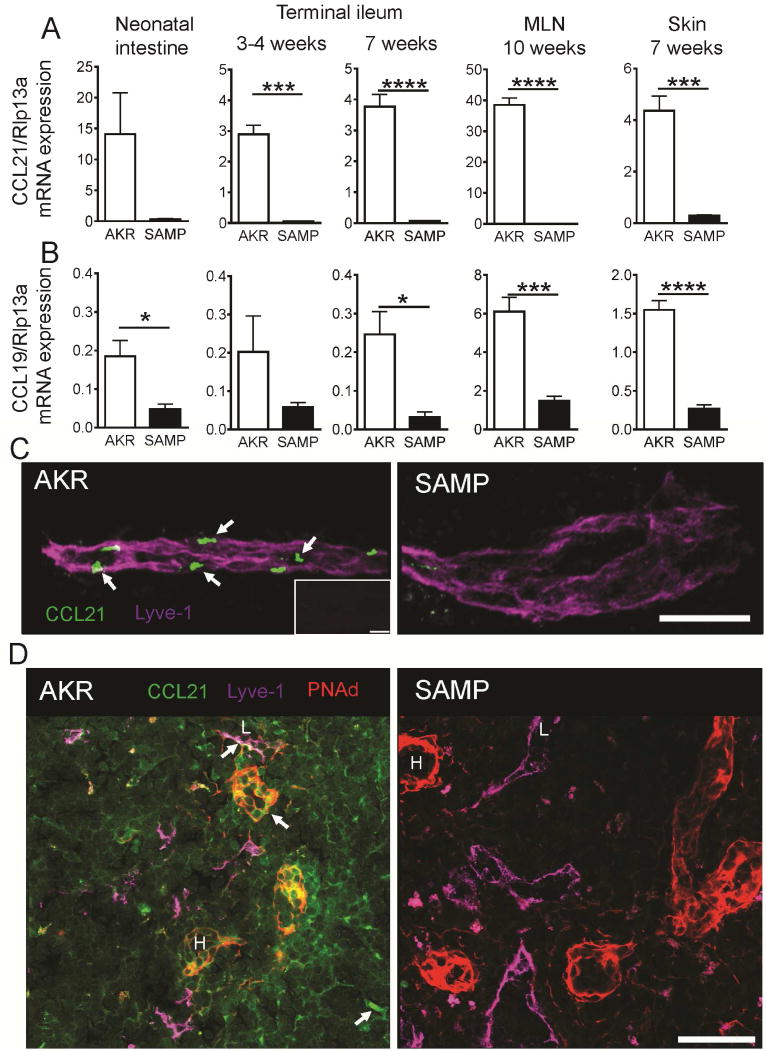
Figure 3. Reduced CCL21 expression in SAMP mice.
Quantitative RT-PCR for CCL21 (A) and CCL19 (B) in neonatal intestine, terminal ileum, mesenteric lymph nodes and skin of AKR and SAMP mice; mean±SEM for n=3–5 mice/group. Ribosomal protein L13A (Rpl13a) mRNA was used as a reference. (C) Whole mount staining of terminal ileum with antibodies to CCL21 (green) and Lyve1 (magenta). Confocal immunofluorescence demonstrates abundant presence of CCL21 protein (arrows) in Lyve1+ lymphatic vessel of AKR, while weak expression of CCL21 can be seen only sporadically in SAMP mice; Maximum intensity projection of 15 × 1 μm Z stacks. Bar = 100 μm Representative of 3 experiments with total n=4 mice/strain. Isotype control is shown in the insert. Bar = 30 μm. (D) Sections of MLN form AKR and SAMP mice were stained with antibodies to CCL21 (green), peripheral node addressin (red) and Lyve-1 (magenta). Diffuse and concentrated (arrows) pools of CCL21 in lymphatic vessels (L) and high endothelial venules (H) are absent in SAMP lymph nodes. Bar = 50 μm. Representative of 2 experiments.