Figure 4.
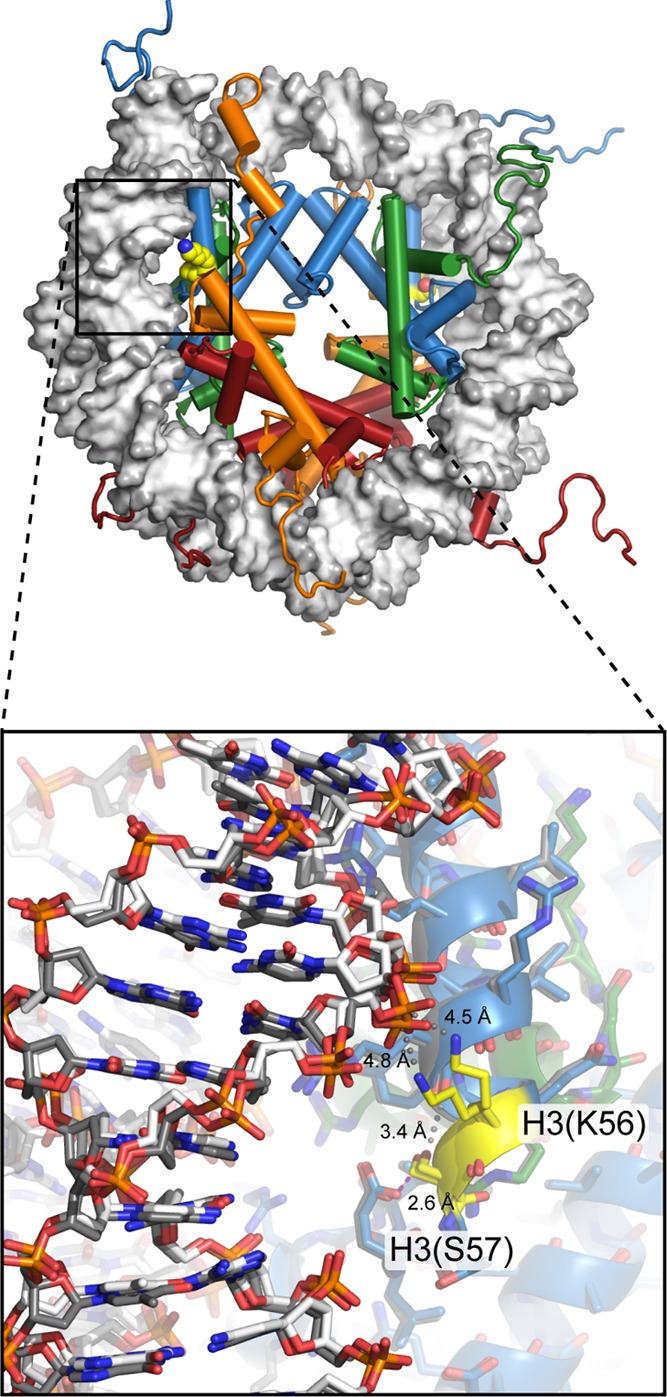
View of the nucleosome (1KX5), with H3(K56) and H3(S57) highlighted in yellow. Located under the DNA near the nucleosome entry/exit region, H3(K56ac) increases site exposure by increasing the DNA unwrapping rate52,61 and influences histone chaperone binding,126 while H3(S57A) substitution interferes with octamer formation and increases H2A/H2B dimer exchange.90 Close-up view (bottom) shows the two sides of the nucleosome superimposed, with one copy of each histone in color and one copy in gray. In the crystal structure, H3(S57) hydrogen bonds with neighboring H3(E59) (magenta dotted line) and makes van der Waals contacts with carbonyl oxygens of the αN-helix of histone H3 (gray spheres) but is too far to make direct interactions with DNA. Although the neighboring H3(K56) makes a closer approach to DNA, the lysine side chain is too distant to directly hydrogen-bond to the phosphate backbone. The two positions observed for the H3(K56) side chain suggest some mobility, and the small gray spheres highlight the shortest path from the lysine to the closest DNA phosphates.
