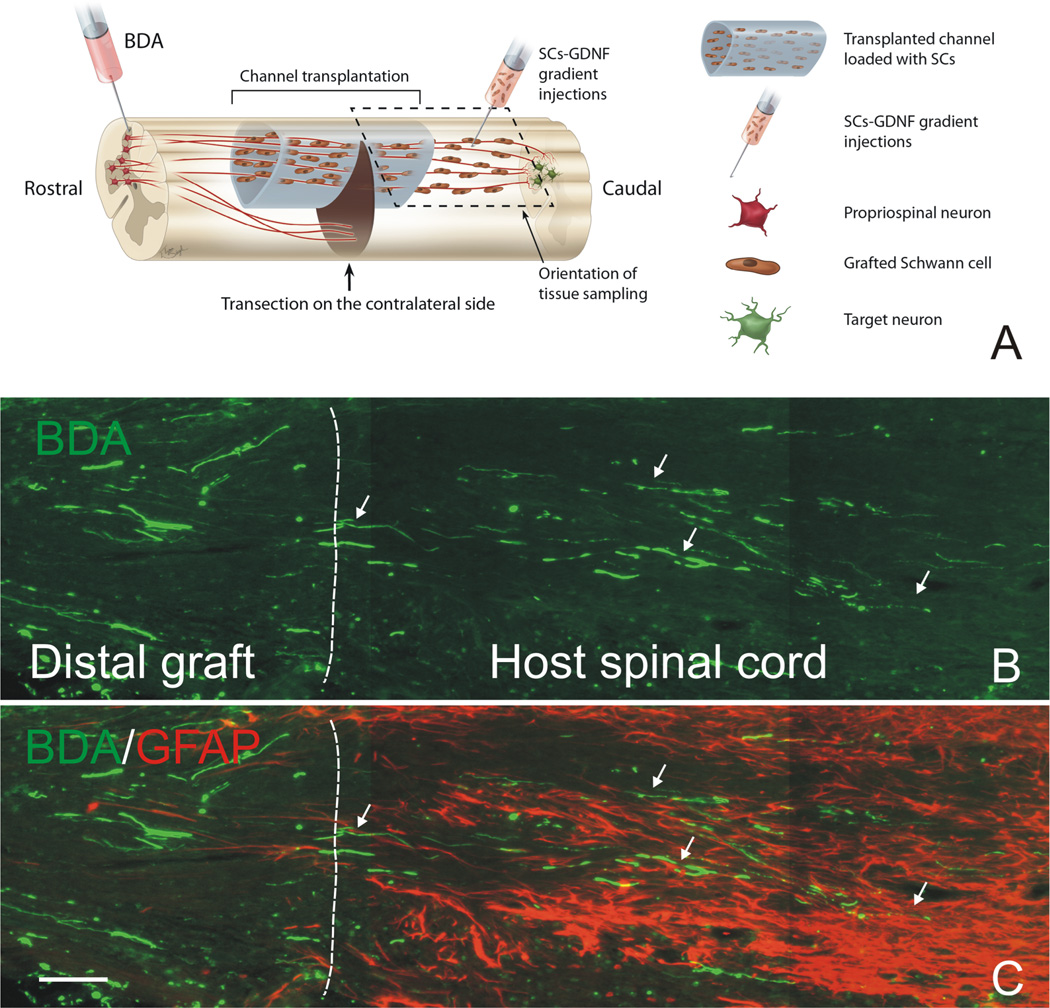
Figure 3. Descending propriospinal axons regenerate across the caudal graft-host interface and grew back into the distal host spinal cord.
(A) Schematic drawing shows the experimental strategy and how tissue was sampled. Note that a continuous growth permissive pathway was established by graft of Schwann cell over-expressing GDNF (SCs-GDNF) both in the lesion and caudal spinal cord to promote the axonal regrowth beyond the graft-host interface. (B) BDA-anterogradely labeled propriospinal axons (green, arrows) were found to penetrate through the distal graft-host interface (white dashed line) and to elongate within the distal host spinal cord only in the group injected with SCs-GDNF into the caudal host tissue. (C) The distal graft-host interface was demarcated by GFAP-labeled astrocytes (red). B&C Scale Bar=100µ m. Modified from Deng et al. (2013).