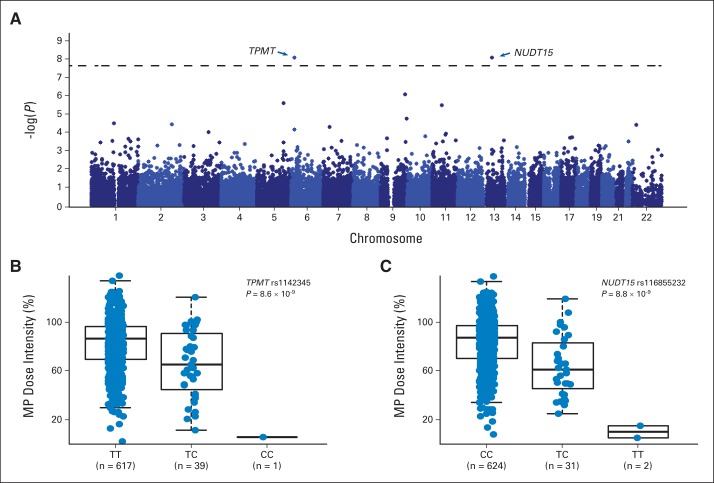
Fig 2.
Genome-wide association study identified TPMT and NUDT15 variants associated with mercaptopurine (MP) dose intensity. (A) Total of 40,889 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were tested for associations with MP dose intensity in 657 children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in AALL03N1 cohort. Association P value (y-axis) is plotted against respective chromosomal position of each SNP (x-axis). Dashed horizontal line indicates genome-wide significance threshold (P < 5 × 10−8). TPMT and NUDT15 loci are indicated by arrows. MP dose intensity was significantly lower for patients heterozygous or homozygous for risk alleles at (B) TPMT SNP rs1142345 (contributing to *3A and *3C) and (C) NUDT15 SNP rs116855232, compared with those with wild-type genotypes. P value was estimated using linear mixed-effects model, with genetic ancestry as covariate. Each box includes data between 25th and 75th percentiles, with horizontal line indicating median. Whiskers indicate maximal and minimal observations within 1.5× length of box.