Figure 3.
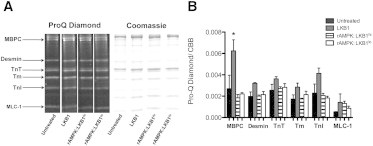
ProQ Diamond phosphoprotein stain after treatment with and without various activated AMPKs and the LKB1 complex. (A) Representative lanes (n = 4 per treatment group) from the same gel stained first for phosphorylation (ProQ Diamond) and then for total protein content (Coommassie Brilliant Blue). Protein identification as shown on the left was based on the molecular weights of known myofibrillar proteins. (B) The relative optical density of the phosphoprotein signal was normalized for loading by dividing the ProQ Diamond signal by the corresponding Coomassie Brilliant Blue signal per protein. There is a significant increase in phosphorylation of MBPC in skinned trabeculae treated with only exogenous LKB1 complex compared with all other groups (p < 0.05; n = 4 per group). In all other proteins, there is no significant change in global phosphorylation status.
