Figure 2.
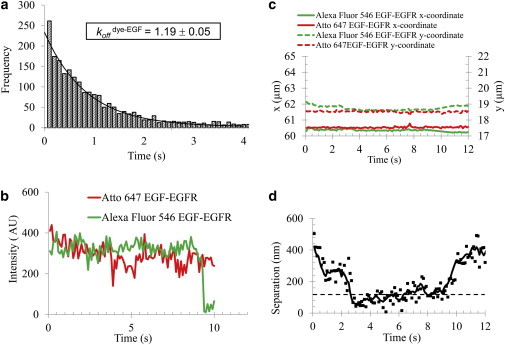
Kinetic analysis of EGFR homodimer dissociation. (a) Distribution of EGFR homodimer lifetimes after EGF stimulation for all accumulated data acquired in five individual experiments employing various TKIs (gefitinib, lapatinib, and AZD 8931). The distribution of more than 2000 dimerization events was fitted to a monoexponential where kappEGF = 1.19 ± 0.05 s−1. (b) Two-color fluorescence emission corresponding to a pair of colocalized molecules labeled with Alexa Fluor 546 (green) and Atto 647 (red), respectively. (c) Changes with time of the horizontal and vertical positions of the dimerization partners. The two molecules temporally coexist between ∼0 and 12 s from the beginning of the measurement. Dimer formation implies simultaneous detection of both molecules at the same time (temporal colocalization) and same location (spatial colocalization). The horizontal and vertical feature positions report on the molecules’ spatial colocalization. (d) The separation distance between the two-color monomers in proximity to each other decreases below the threshold and marks the start of the dimerization event. For the duration of the dimerization event, the separation distance remains under the threshold, followed by a stepwise increase above the threshold upon dimer dissociation. This allows us to extract the apparent duration of an individual dimerization event, τapp. The photobleaching corrected colocalization duration provides the τon for the EGFR homodimer and the corresponding dissociation rate koff. To see this figure in color, go online.
