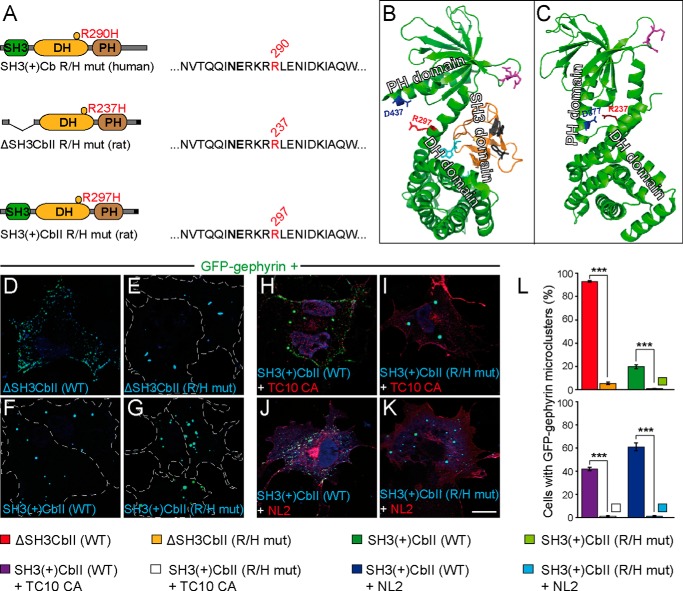
FIGURE 1.
The R/H mutation impairs Cb-mediated submembraneous clustering of GFP-Gephyrin in COS7 cells. A, schematic representation of the human SH3(+)Cb R290H mutant and the corresponding mutants of rat ΔSH3CbII (R237H) and rat SH3(+)CbII (R297H) used in this study. Amino acids surrounding Arg-290 (red) in the primary sequence of human Cb and the corresponding residues in the rat isoforms are shown. The affected arginine residue is located within the catalytic core of the DH domain, in close proximity to the highly conserved Asn-285/Glu-286 residues (bold) that are essential for exchange activity. B and C, three-dimensional structures of rat SH3(+)CbII (B) according to Soykan et al. (Ref. 14; PDB code 4MT6) and ΔSH3CbII (C) according to Xiang et al. (Ref. 30; PDB code 2DFK). The arginine affected in the R/H mutation (red) interacts with Asp-377 in the PH domain of ΔSH3CbII (C). The corresponding aspartate within the PH domain of SH3(+)CbII is Asp-437 (B, red). Arginine residues within the β3-β4 loop of the PH domain (B and C, magenta) that were shown to be involved in PI3P binding (17) are indicated. The SH3 domain (B, orange) forms an intramolecular interface within the DH and PH domains that has been shown to interfere with PI3P binding (14). Cyan and gray residues within the SH3 domain contribute to SH3-DH/PH and SH3-NL2 interactions, respectively (14). Note that the locations of Asp-437 and Arg-297 are on opposite sides of the SH3-DH/PH interface (B). D–K, images of COS7 cells transfected as indicated. GFP-Gephyrin accumulates in large cytoplasmic aggregates when expressed together with Myc-SH3(+)CbII (F). In contrast, in the presence of Myc-ΔSH3CbII (D), GFP-Gephyrin forms microclusters at the plasma membrane. Similarly, Myc-SH3(+)CbII and constitutively active HA-TC10 (TC10 CA), or Myc-SH3(+)CbII and HA-NL2 jointly trigger GFP-Gephyrin microcluster formation (H and J), as described previously (16, 19). Notably, the R/H mutation prevents both the ability of ΔSH3CbII to induce GFP-Gephyrin microclusters (E) and the ability of TC10 CA and NL2 to trigger SH3(+)CbII-mediated Gephyrin redistribution (I and K). The following antibodies were used: polyclonal rabbit anti-HA (1:2,000; Zymed Laboratories Inc., Invitrogen) and monoclonal mouse anti-c-Myc clone 9E10 (1:1,000; Sigma-Aldrich). Dotted lines indicate the cell borders. Scale bar, 10 μm. L, percentages of GFP-Gephyrin cotransfected cells classified as displaying GFP-Gephyrin microclusters (> 50 puncta per cell; n = 3 independent transfections; n = 300 cells). The data represent means ± S.E. ***, p < 0.001; unpaired, two-tailed Student's t test.