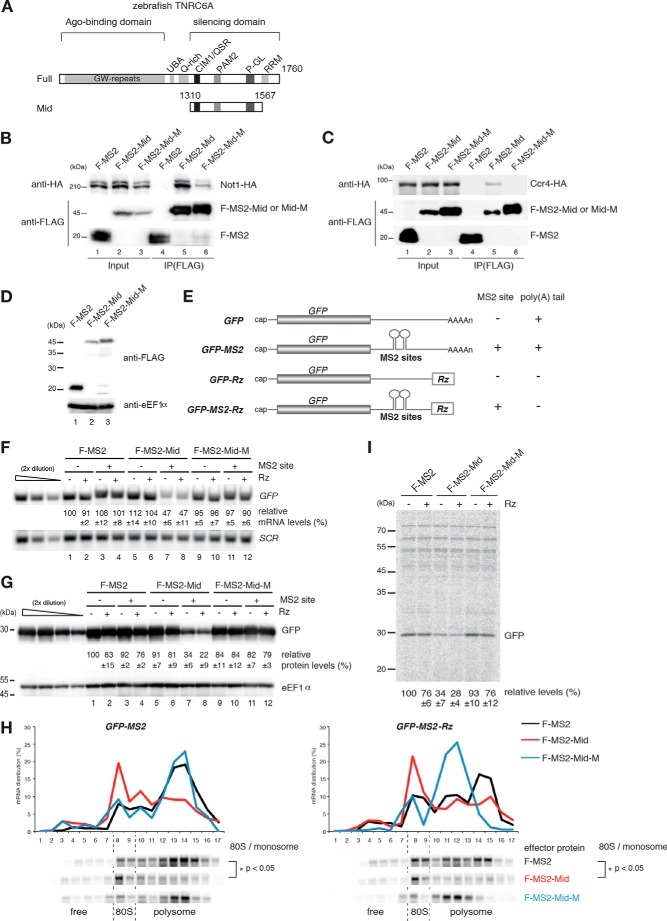
FIGURE 1.
Tethered TNRC6A recapitulates hallmarks of miRNA-mediated gene silencing in S. cerevisiae. A, schematic structures of zebrafish TNRC6A and its Mid domain. B and C, interaction of FLAG-MS2-TNRC6A Mid with yeast Not1-HA and Ccr4-HA. Cell lysates of wild type cells transformed with the indicated plasmids were immunoprecipitated using anti-FLAG antibody. Total extracts (Input) and immunoprecipitates (IP) were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody. D, the expression of the Mid domain of zebrafish TNRC6A in yeast. FLAG-tagged effector proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-FLAG antibody. F-MS2, FLAG-MS2 protein; F-MS2-Mid, FLAG-MS2-TNRC6Amid fusion protein; F-MS2-Mid-M, FLAG-MS2-TNRC6Amid QSR and W mutant fusion protein. This mutant contains the mutations that disrupt the interaction of Not1 with TNRC6. E, schematic drawing of reporter genes used in Fig. 1. The filled box indicates the open reading frame. All reporter genes contain the 3′-UTR region of PGK1, in which two tandem MS2 binding sites were inserted. Rz, a hammerhead ribozyme that generates a 3′ end with no poly(A) tail. F, tethering of TNRC6A reduces mRNA levels independently of a poly(A) tail. RNA samples from wild type cells transformed with the indicated plasmids were analyzed by Northern blotting using GFP and SCR probes. The data represent the means of three independent experiments, with S.D. values. G, tethering of TNRC6Amid reduces protein levels independently of a poly(A) tail. Wild type cells harboring the indicated plasmids were grown, and protein samples were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-GFP antibody. eEF1α served as a loading control. The data represent the means of three independent experiments with S.D. values. H, tethering of TNRC6A induces translation repression, dependent on interaction with Not1 but independent of a poly(A) tail. Cell extracts were prepared from wild type cells transformed with the indicated plasmids, and polysome analysis was performed. Top, ratio (%) of mRNA distribution in each fraction. Bottom, reporter mRNA was detected by Northern blotting using a PGK1 3′UTR probe. The p value was calculated by using Student's t test. I, levels of synthesized GFP derived from reporter mRNAs were significantly reduced by tethered TNRC6 independently of a poly(A) tail. Pulse-labeling experiments were performed using the same cells as in F. GFP-MS2 and GFP-MS2-Rz protein levels are shown as the mean values of three independent experiments with S.D. values.