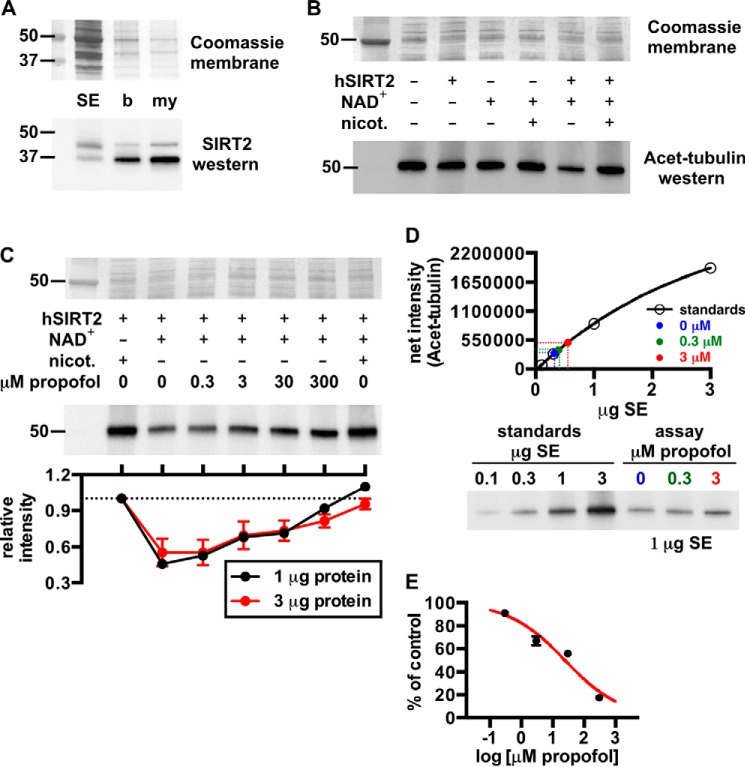
FIGURE 5.
A, Western blot showing relative amounts of SIRT2 in rat brain fractions: SE, soluble brain extract; b, brain homogenate; my, myelin. The Coomassie R-250-stained membrane is shown for loading. B, Western blot demonstrating deacetylation of acetylated α-tubulin (Acet-tubulin) from rat brain by recombinant human SIRT2 (hSIRT2). In this assay, SIRT2 activity was pronounced with the addition of 3 μg of SIRT2 and 1 mm NAD+, and deacetylase activity was inhibited by the SIRT2 inhibitor nicotinamide (nicot.); the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A was added to all reactions. 3 μg of soluble extract protein from an assay was loaded in each lane for this blot. C, propofol concentration-dependently inhibited SIRT2 deacetylation of acetylated α-tubulin. Assays were performed similar to B with the indicated substrates ± propofol. D, representative standard curve from a Western blot used to determine absolute levels of acetylated α-tubulin deacetylation by SIRT2 in the absence and presence of propofol. For this, increasing amounts of soluble brain extract protein were separated via SDS-PAGE, and alongside this, 1 μg of protein from SIRT2 deacetylase assays that contained no inhibitor, 0.3 μm propofol, or 3 μm propofol was separated. Densitometry from the standards allowed generation of the standard curve, from which absolute levels of deacetylase activity in the assay samples were determined. In this assay, 0.3 and 3 μm propofol inhibited SIRT2 activity by 9 ± 1 and 33 ± 4%, respectively. E, from the tubulin deacetylase assays, the absolute levels of SIRT2 inhibition at each propofol concentration are shown and were used to fit the sigmoidal curve drawn in red; 25 ± 2 μm propofol was necessary to inhibit the enzyme by 50%, and the slope of the curve was equal to −0.5 ± 0.1. Mean values are shown with S.E.