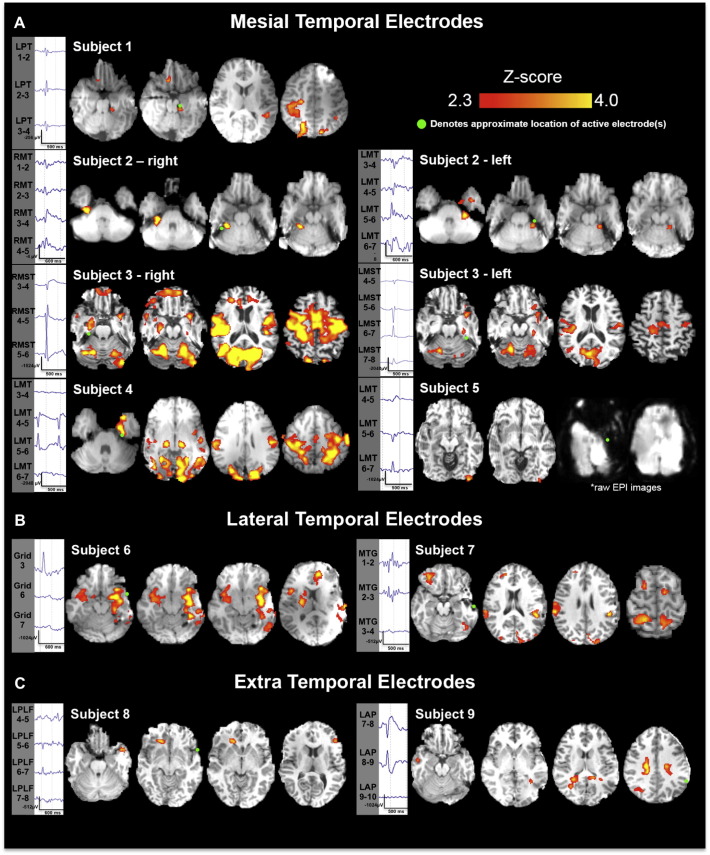
Fig. 2.
Significant BOLD clusters associated with interictal discharges recorded via simultaneous iEEG-fMRI. (A) Mesial temporal lobe patients. Significant BOLD clusters (p < 0.05, AlphaSim correction) were found in all 5 subjects in this group. Two patients had independent, bilateral temporal discharges that were modeled independently of one another providing 7 datasets for analysis. A significant cluster is found adjacent to the active intracranial electrode contact (marked by a green circle) in 6/7 analyses. One patient (subject 5), had a large amount of susceptibility artifact in the left temporal lobe associated with a large amount of subject motion during data collection. (B) Lateral temporal lobe patients. Significant BOLD clusters (p < 0.05, AlphaSim correction) were found in both patients in this group. A significant cluster was found adjacent to the active intracranial electrode contact (green circle) in 1 of 2 analyses. (C) Extratemporal patients. Two patients with extra-temporal lobe epilepsy showed no significant clusters adjacent to the active electrode(s).