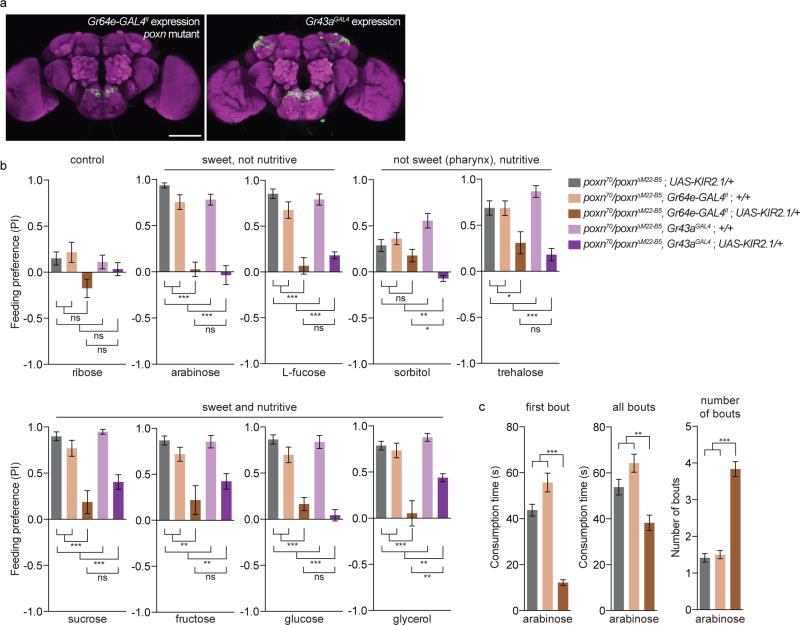
Figure 5.
Pharyngeal GRNs are necessary for the preference of poxn mutants for sweet compounds (a) Immunofluorescence of anti-GFP (green) and nc82 (magenta), showing expression of the Gr64e-GAL4II and Gr43aGAL4 drivers used in the behavioural experiments shown. Gr64e-GAL4 is shown in a poxn null mutant background, while Gr43aGAL4 is in a poxn/+ heterozygous background. Scale bars are 100 μm. (b) Preference of indicated genotypes for 100 mM solutions of the specified compounds in 1% agar (positive) versus agar alone (negative). (c) Temporal consumption characteristics of the indicated genotypes in response to stimulation with 50 mM arabinose. Values represent mean +/− s.e.m. for n = 10 groups of 10 flies each in b and n = 29-60 flies in c, with independent replicates performed over at least 2 days. Asterisks indicate significant difference by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns = not significant.