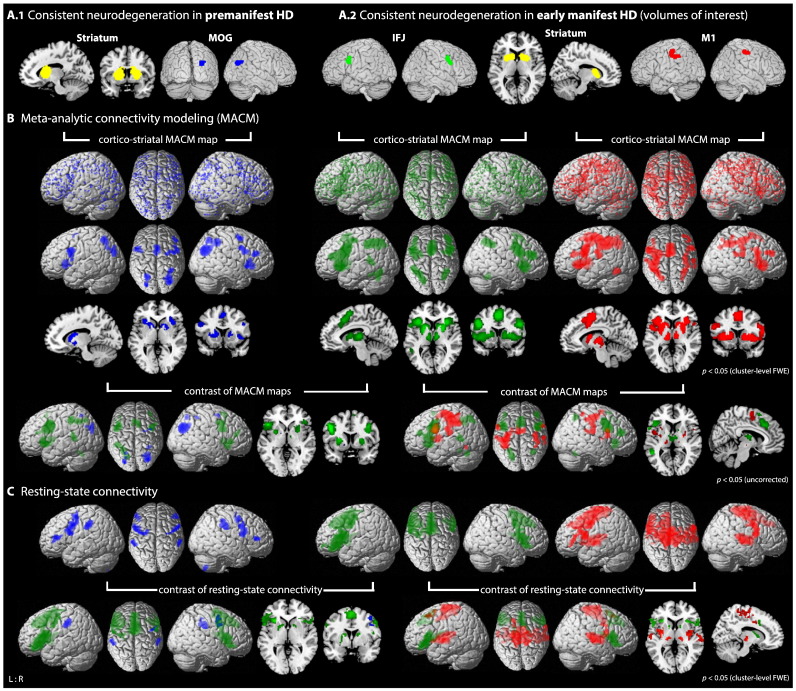
Fig. 2.
Functional connectivity modeling of consistent cortico-striatal atrophy in premanifest and manifest HD. A) Location of the seed regions showing convergent evidence of atrophy as revealed by coordinate-based meta-analysis across voxel-based morphometry studies in HD (Dogan et al., 2013): A.1 in premanifest HD located in the striatum (cluster maxima [x/y/z in MNI]: right 26/8/8; left −32/−12/−8 and −14/6/14) and right middle occipital gyrus (MOG; 30/−72/28); A.2 in manifest HD located in the striatum (right 24/6/10; left −10/12/8), inferior frontal junction (IFJ; right 40/2/38; left −42/8/28) and motor cortex (M1; right 34/−24/52; left −34/−28/52). B) Brain-wide co-activation maps of the respective cortical seeds in conjunction with striatal seeds as revealed by MACM (blue: MOG-striatal map; green: IFJ-striatal map; red: M1-striatal map): 1st panel: Brain-wide foci reported in BrainMap that featured the activation peaks closest to the respective seed voxels; these foci are modeled by 3D Gaussian reflecting uncertainty of their location using ALE meta-analysis. 2nd/3rd panel: above-chance convergence indicates significant co-activations with the respective seed region. 4th panel: contrast analysis between MACM maps showing differences in brain-wide co-activations patterns (blue: MOG-striatal map > IFJ-striatal map; green — left side: IFJ-striatal map > MOG-striatal map; green — right side: IFJ-striatal map > M1-striatal map; red: M1-striatal map > IFJ-striatal map). C) 1st panel: resting-state connectivity of the respective cortical seeds in conjunction with striatal seeds. 2nd panel: contrast analysis between resting-state connectivity (see above for color coding).