Figure 2.
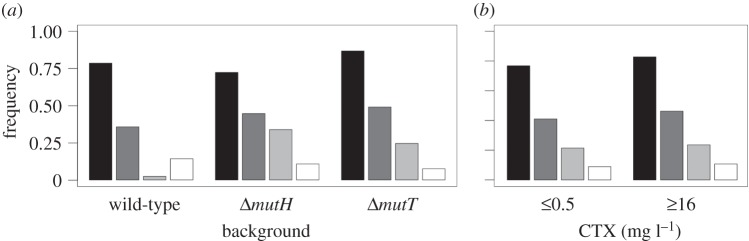
Phenotypic profiles of representative evolved clones. Bars represent the frequency of isolates displaying alterations in permeability (black), efflux (dark grey) and erythromycin hypersusceptibility (light grey). White bars correspond to isolates without alterations. (a) Phenotypic profiles of wild-type and mutator strains. Only differences in erythromycin hypersusceptibility were found to be statistically significant (see main text). (b) Phenotypic profiles according to the antibiotic concentration from which the clones were isolated. No statistically significant differences between early and late clones were observed. These results suggest that general multi-drug resistance evolved early and in parallel across the different backgrounds, and therefore is not sufficient to explain the final survival patterns.
