Figure 1.
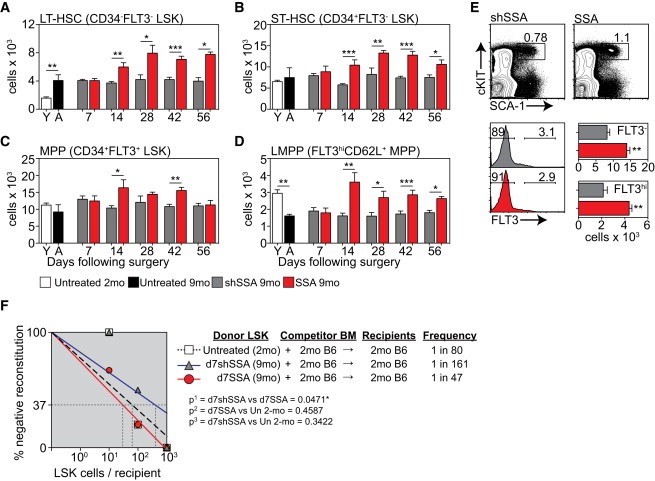
SSA Increases the Number of Multilineage HSCs in Middle-Aged Mice
(A–D) Lin−SCA1+cKIT+ (LSK) BM can be subdivided into populations of LT-HSCs (CD34−FLT3−), ST-HSCs (CD34+FLT3−), and MPPs (CD34+FLT3+). The MPP population can be further fractionated based on FLT3 and CD62L expression for analysis of LMPPs (FLT3hiCD62L+). Absolute number of LT-HSCs (A), ST-HSCs (B), MPPs (C), and LMPPs (D) (n = 5–12/group/time point).
(E) Concatenated flow cytometry plots, gated on Lineage− cells, and absolute number of FLT3− LSK cells, 1 year after surgical SSA of 9-month male mice (n = 5/group).
(F) LSK cells were FACS purified from untreated CD45.2+ 2-month; CD45.2+ 9-month mice 7 days following surgical shSSA (d7shSSA); or CD45.2+ 9-month mice 7 days following surgical SSA (d7SSA) (n = 6 recipients/group/dose) and graded doses of cells were transferred into lethally irradiated congenic CD45.1 recipients along with 5 × 105 CD45.1+ supporting BM cells. Multilineage reconstitution (>1% B cell, T cell, macrophage, and granulocyte) was analyzed 12 weeks after transplant and the frequency of repopulating cells was calculated by Poisson statistics.
Bar graphs represent mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figures S1 and S2.
