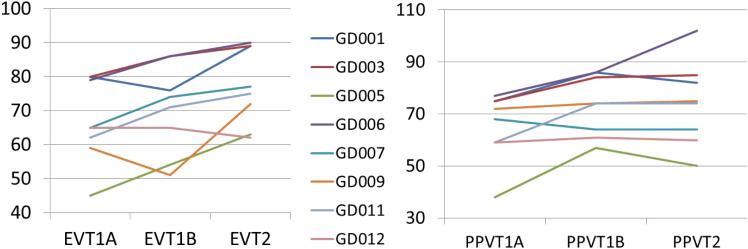
Figure 5. Neuropsychological indices in G1D patients after triheptanoin food supplementation.
Vocabulary performance improved acutely and long term with triheptanoin supplementation. The neuropsychological scores of all 8 G1D subjects before and after triheptanoin are represented. Subject designations are the same through all the figures and tables. Standardized PPVT and EVT ratings (y-axis) were obtained in the fasting state (baseline) at time 0 min (x-axis 1A suffix) and 60 min (x-axis 1B suffix) following triheptanoin ingestion, and then subsequently after 3 months of daily triheptanoin supplementation (x-axis T2 suffix). PPVT and EVT scores were below normal age ranges and increased at subsequent time points in rigorously statistically significant fashion. The 95% confidence intervals for the PPVT scaled scores at each of the three time points studies were 54.4 - 76.3; 63.6 - 82.9 and 60.4 - 87.6, respectively. PPVT scores improved significantly over time (F2,14 = 5.945, p=0.014), although there were no significant pairwise comparisons after Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons. The 95% confidence intervals for the EVT scaled scores at each of the three time points studies were 56.6 - 77.2; 59.4 - 81.3 and 67.6 - 86.6, respectively. EVT scores improved significantly over time (F2,14 = 9.571, p=0.002). Pairwise comparisons yielded (pre-oil relative to follow-up) p=0.006 (Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons).