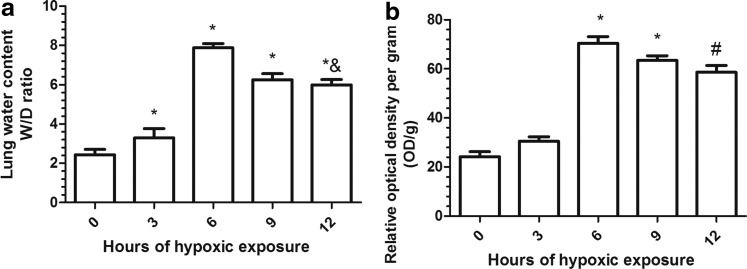
FIG. 1.
Effect of hypobaric hypoxia on (a) lung water content and (b) pulmonary vascular leakage in mice. Mice were exposed to simulated hypoxia for different time points. The water content was determined using wet-to-dry ratio, and pulmonary vascular leakage was determined using Evans Blue. The maximum water content and pulmonary vascular leakage were obtained at 6 h after hypoxic exposure, indicating that pulmonary edema was induced at this time point. Values are mean±SD (n=10). Significant differences between groups were determined by analysis of variance followed by Student-Newman-Keuls test. #p<0.05, compared with control group (0 h), *p<0.01 compared with control group (0 h), &p<0.05 compared with hypoxia group (6 h).