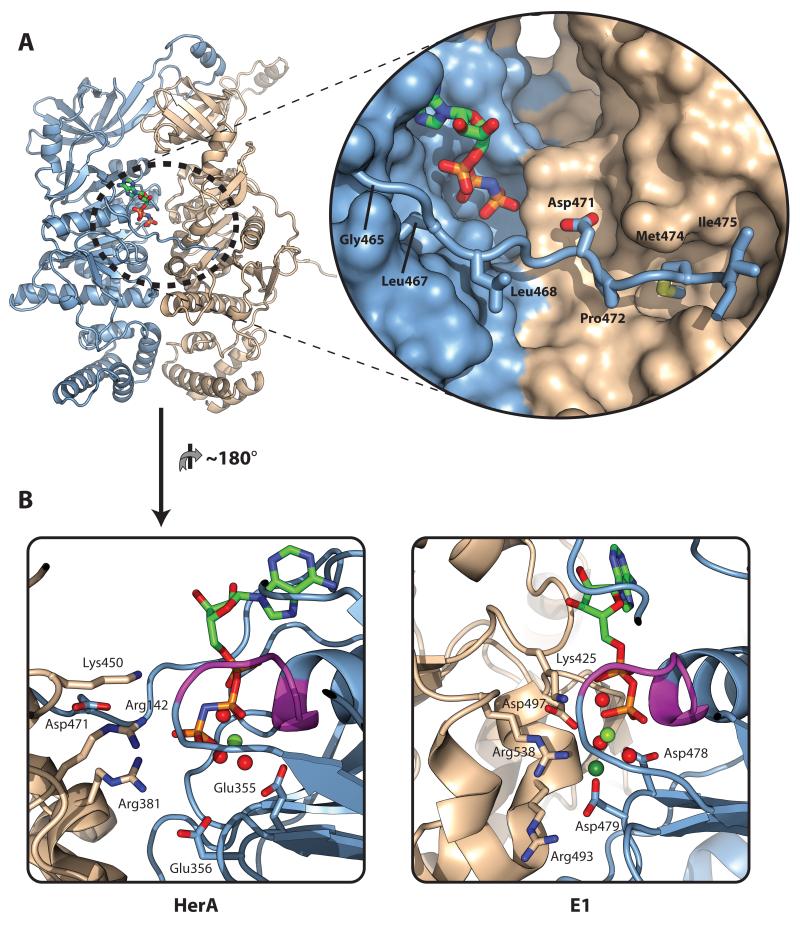
Figure 3. A C-terminal brace associates with the ATP-binding site.
(A) Left; Cartoon representation of the two HerA protomers present in the asymmetric unit. Chain A is coloured light blue; Chain B is coloured wheat. Bound AMP-PNP (stick representation) is located at the interface between protomers. Right (inset); Close-up surface representation of the interface between the protomers, with the bound AMP-PNP shown as sticks. A flexible C-terminal brace from Chain A shown in cartoon format extends across the active site to embrace Chain B. Hydrophobic residues G465, L467, L468, P472, M474 and I475 (shown as sticks) position the brace. The acidic residue D471 protrudes towards the active site. (B) Cartoon comparison of the HerA active site with that of the E1 helicase (PDB id 2GXA) in an ATP-type conformation. Left; HerA active site between Chains A (light blue) and B (wheat), viewed from inside the DNA-binding pore, with bound AMP-PNP and key residues shown as sticks. Bound magnesium and water moieties shown as pale green and red spheres, respectively. Chain A donates the Walker A motif (magenta; sticks omitted), and Walker B motif (E355 and E356). Chain B donates three positively charged residues (from the top, K450, R142 and R381). R381 forms a salt bridge with Walker B glutamate E356, while R142 directly interacts with the γ-phosphate of the ATP-mimic. The conserved acidic brace residue (D471) forms a salt bridge with R142, positioning this arginine at the active site. Right; Comparative view of the E1 ‘ATP-type’ active site between Chains A (light blue) and B (wheat). Key residues and bound ADP shown as sticks. Bound magnesium and water moieties shown as pale green and red spheres respectively, and bound chloride (mimicking ATP γ-phosphate) as a dark green sphere. As in HerA, Chain A donates the Walker A motif (magenta) and Walker B aspartates (D478 and D479), while Chain B donates three positively charged residues (from the top, K425, R538 and R493). A cis-acting aspartate (D497) interacts with the middle of these residues, in a manner similar to the R142/D471 interaction in HerA. All figures generated using PyMOL (57).