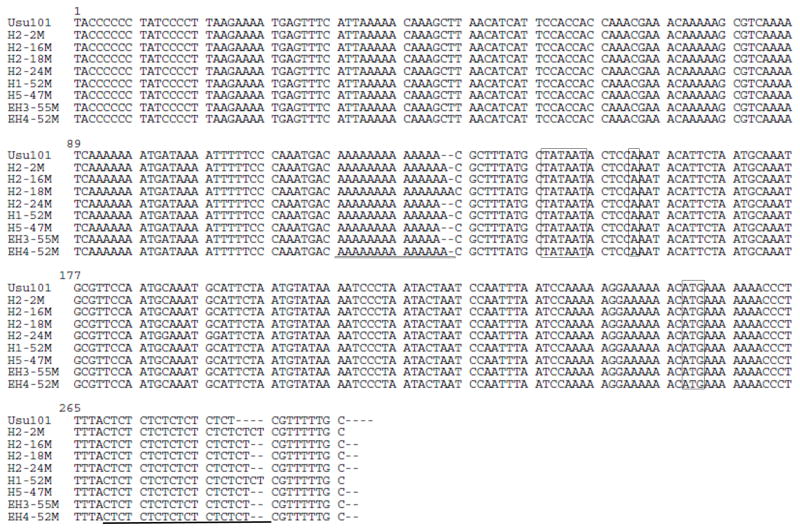
FIG 5. Sequencing of the babA promoter region.
To further assess the loss of BabA expression, the babA promoter region was sequenced for several isolates using primer IR (Table 1). The −10 core promoter element (TATAAT), the +1 transcriptional start site (A), and the ATG translational start codon are boxed. The poly-A tract upstream of the −10 region and the CT repeat region downstream of the translational start site are underlined. In comparison to USU101 (13 A’s, 8 CT’s) the output strains differ in the number of repeats in either one or both of these regions. The lengths of poly-A tracts range from 13 to 15 and the CT repeat lengths range from 8 to 10. The addition of CT repeats, seen in all of the isolates, occurs within the coding region of babA and results in the pre-mature truncation of the protein.