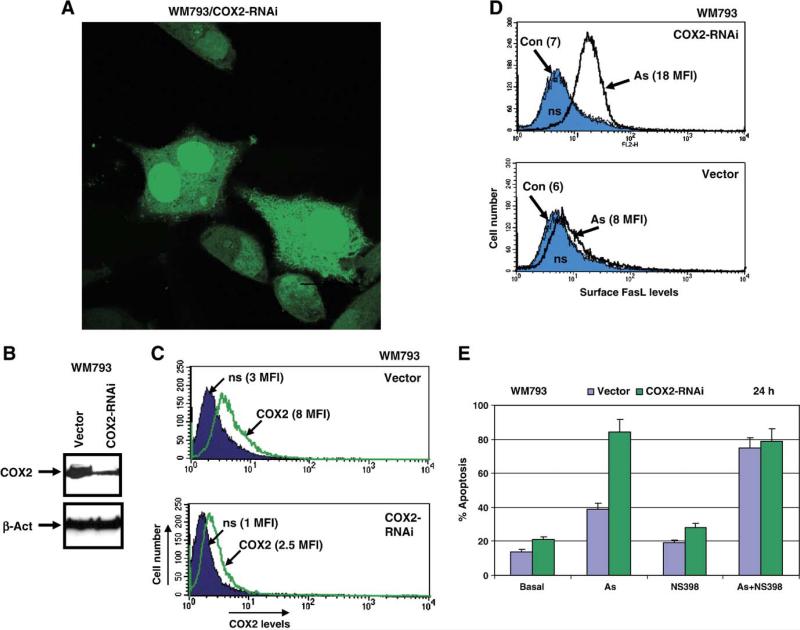
Fig. 7.
Downregulation of COX-2 protein levels by targeting of COX-2 mRNA with specific RNAi of 19 nucleotides leads to upregulation of FasL expression and acceleration of arsenite-induced apoptosis in human melanoma WM793. (A) RNAi, designed to target human COX-2 mRNA within nucleotides 354–372, was expressed using pSR-GFP/Neo (Cox-2-RNAi) vector, which also produced a marker GFP protein. Human melanoma WM793 cell line with moderate basal expression of COX-2 has been used for COX-2 silencing. Two mass cultures of WM793 cells were obtained after transfection with the empty vector or with the COX-2 RNAi expression construct and subsequently selected in the presence of G-418 (400 μg/ml). GFP expression is localized in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus of transfected cells. (B) Total protein levels of COX-2 expression in selected cultures were detected by Western analysis. (C) FACS analysis of transfected and selected cells using monoclonal anti-COX-2 antibody and the secondary anti-mouse Ab labeled with PE confirmed a downregulation of COX-2 levels in WM793/COX-2 RNAi cells from 8 MFI to 2 MFI. (D) Sodium arsenite (As, 5 μM) treatment of control (Vector) and COX-2 knockdown cells dramatically increased surface expression of FasL. FACS analysis was performed as indicated in the legend to Fig. 4. (E) Percentage of Annexin-V-PE-positive (red) apoptotic cells among transfected GFP-positive cells was determined using FACS analysis. Treatment of WM793 cells with arsenite, NS398 or their combination was performed for 12 h.