Figure 2. A self-reinforcing loop linking siRNAs to DNA and histone methylation in A. thaliana.
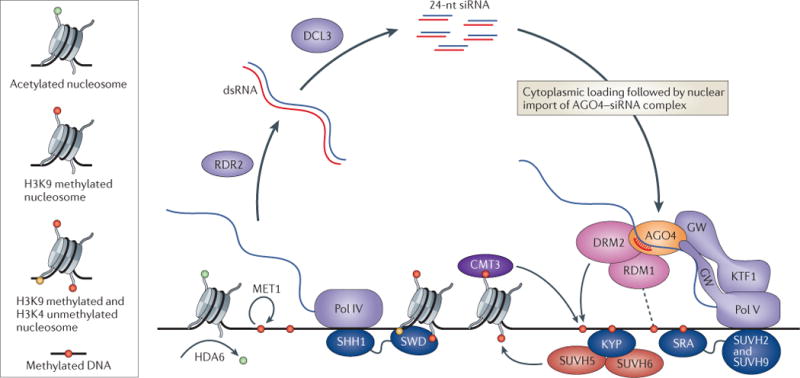
Elaborate feedback between small RNAs and DNA and histone methylation underlies a robust silencing pathway at sites of asymmetrical cytosine methylation in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Two plant-specific polymerases transcribe the critical RNAs. RNA polymerase IV (Pol IV) transcripts are processed by the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RDR2 and the Dicer protein DCL3 into 24-nucleotide (nt) small interfering (siRNAs), while Pol V transcripts act as their targets. The Argonaute protein AGO4, the siRNA-dependent recruitment of which to Pol V transcripts is reinforced by interactions with the GW domains of Pol V and an associated elongation factor KTF1, in turn recruits the CHH DNA methyltransferase DRM2. RDM1 associates with the Pol V–AGO4–DRM2 complex and may link siRNA amplification to pre-existing DNA methylation. Meanwhile, another DNA methyltransferase that targets CHG sites for maintenance, CMT3, is recruited directly to methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9). Silencing by DNA methylation is augmented by H3K9 methylation, which is deposited by the enzymes KYP, SUVH5 and SUVH6. These methylation events are coupled to one another and to siRNA activity in several ways. KYP is recruited directly to methylated DNA, where it methylates neighbouring histones, and the H3K9 methylation reader SHH1 recruits Pol IV to promote siRNA generation, while the DNA methylation readers SUVH2 and SUVH9 recruit Pol V to promote AGO4 targeting and further DNA methylation. Thus, the different methylation readers, RNA polymerases and AGO4 act together to create self-reinforcing interactions between pre-existing DNA methylation and siRNA amplification. Erasure of DNA methylation by mutations in either the histone deacetylase HDA6 or the maintenance DNA methyltransferase MET1 results in loss of siRNA biogenesis, emphasizing the importance of these self-enforcing interactions. Altogether, the A. thaliana pathway for DNA methylation at asymmetrical sites is one of the most remarkable examples of a recurring theme in epigenetic regulation by small RNAs: self-reinforcing feedback loops. SRA, SET and RING finger-associated; SWD, SAWADEE domain.
