Figure 6.
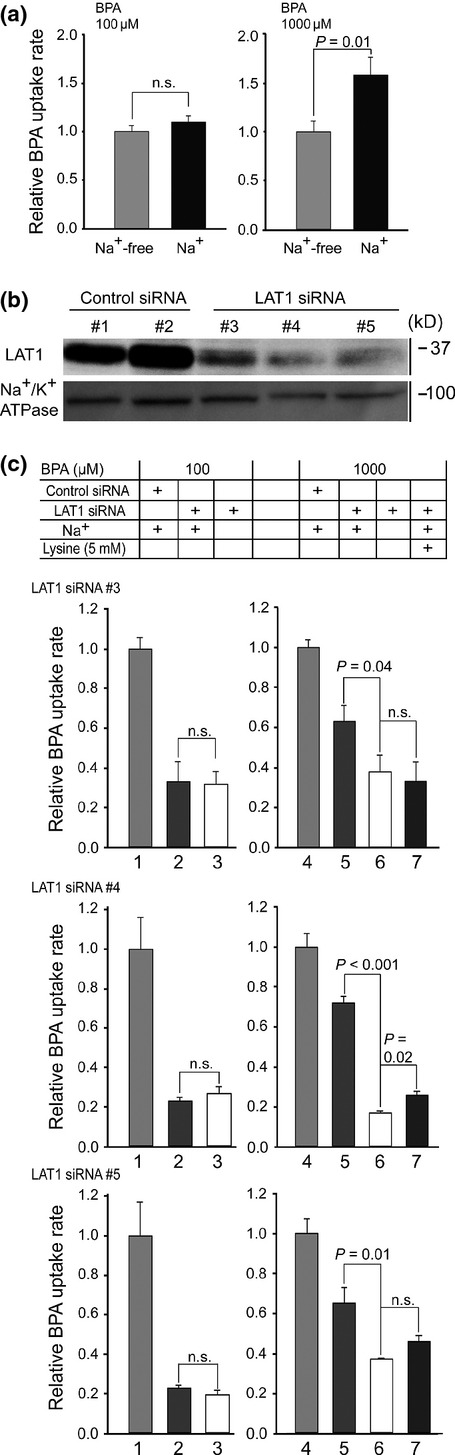
Differential roles of ATB0,+ and LAT1 in p-boronophenylalanine (BPA) uptake. (a) Uptake of BPA in MCF-7 cells was measured for 10 min at 100 μM (left) and 1000 μM (right) BPA. At 1000 μM, the uptake rate in the presence of Na+ increased by ∽1.4-fold from the Na+-free uptake. (b) MCF-7 cells were transfected with non-targeting control siRNA #1 and #2, and LAT1-targeting siRNA #3, #4 and #5. The siRNAs #3–#5 achieved a ∽80% reduction of LAT1 protein amount. (c) Uptake by ATB0,+ was separated by LAT1 knockdown and lysine inhibition. The uptakes in the presence of Na+ and with mock knockdown were set at 1.0 at each BPA concentration (bars 1 and 4). At 100 μM BPA, the uptake levels with LAT1 knockdown did not differ regardless of Na+ (bars 2 and 3). At 1000 μM, LAT1 knockdown left a significant Na+-dependent component (bars 5 and 6). Overall, although with various statistical significances, the BPA uptake in bar 5 was inhibited by 5 mM lysine to a level similar to bar 6 (bar 7). This Na+-dependent and lysine-inhibitable component accounted for at least 20–25% of the total uptake. siRNA#1 was used for control siRNA. n.s., not significant.
