Figure 2.
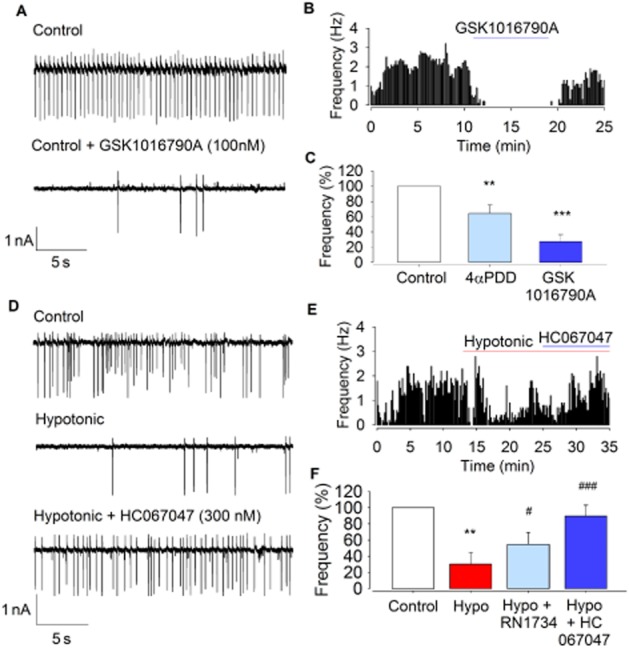
The effect of TRPV4 channel modulators on ACf. (A) Raw action current trace at 300 mOsm (control) with and without the selective agonist GSK1016790A (100 nM). (B) Representative frequency histogram showing action current responses to GSK1016790A. (C) ACf from experiments similar to those illustrated in (A) and (B) is significantly reduced upon addition of 4αPDD (n = 6) or GSK1016790A (n = 8). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, signficantly different from control. (D) Raw action current trace at 300 mOsm (control), 270 mOsm (hypotonic) and with the addition of the TRPV4 channel antagonist HC067047 (300 nM). (E) Representative frequency histogram showing recovery of ACf upon HC067047 addition, after loss from hypotonic challenge. (F) Mean ACf from experiments similar to those illustrated in (D) and (E) is significantly reduced upon hypotonic challenge but not in the presence of RN1734 or HC101679A, both of which showed a significant difference to hypotonic alone. This further suggests a role for TRPV4 channels in osmosensation. **P < 0.01, signficantly different from control; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001, signficantly different from hypotonic alone; n = 6.
