Figure 4.
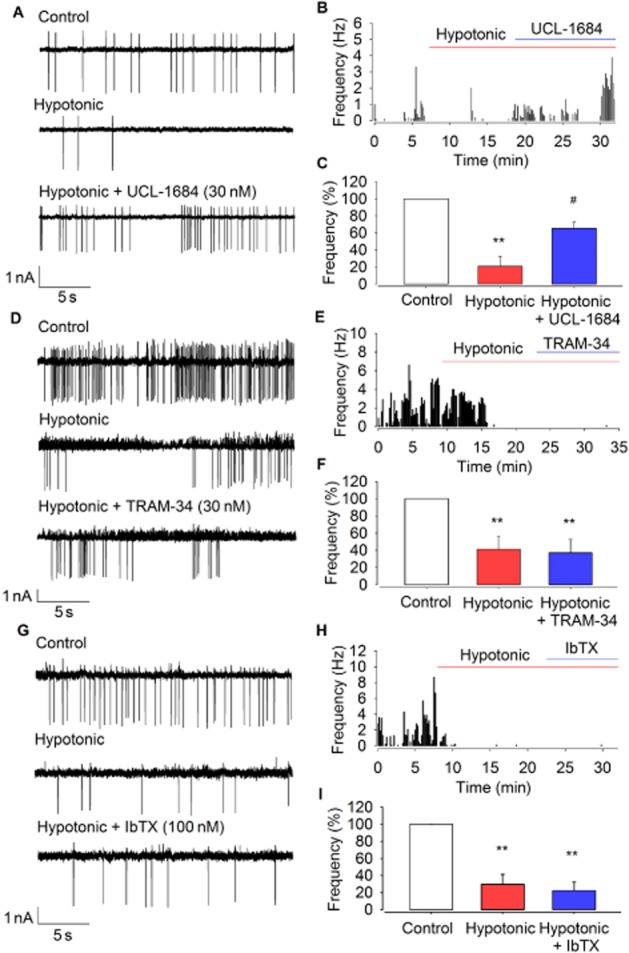
The effect of KCa channel inhibitors on osmotic sensitivity of PVN neurones. (A) Raw action current trace at 300 mOsm (control), 270 mOsm (hypotonic) and with the addition of the SK inhibitor UCL-1684 (30 nm). (B) Representative frequency histogram showing regain of ACf upon UCL-1684 addition after loss from hypotonic challenge. (C) Mean ACf from experiments similar to those illustrated in (A) and (B) is significantly reduced at 270 mOsm, but not in the presence of the SK channel inhibitor (n = 5). **P < 0.01, signficantly different from control; #P < 0.05, signficantly different from hypotonic alone. (D) Raw action current trace at 300 mOsm, 270 mOsm and with the addition of the IK channel inhibitor TRAM-34 (30 nm). (E) Representative frequency histogram showing TRAM-34 has no effect on ACf (F) Mean ACf from experiments similar to those illustrated in (D) and (E) is significantly reduced upon hypotonic challenge and this response is unchanged upon addition of TRAM-34 (n = 5). **P < 0.01, signficantly different from control. (G) Raw action current trace at 300 mOsm, 270 mOsm and with the addition of the BK channel inhibitor iberiotoxin (IbTX) (10 nm). (H) Representative frequency histogram showing IbTX has no effect on ACf. (I) Mean ACf from experiments similar to those illustrated in (G), and (H) is significantly reduced upon hypotonic challenge; osmotic sensitivity is unchanged upon addition of IbTX (n = 6). **P < 0.01, signficantly different from control.
