Figure 4.
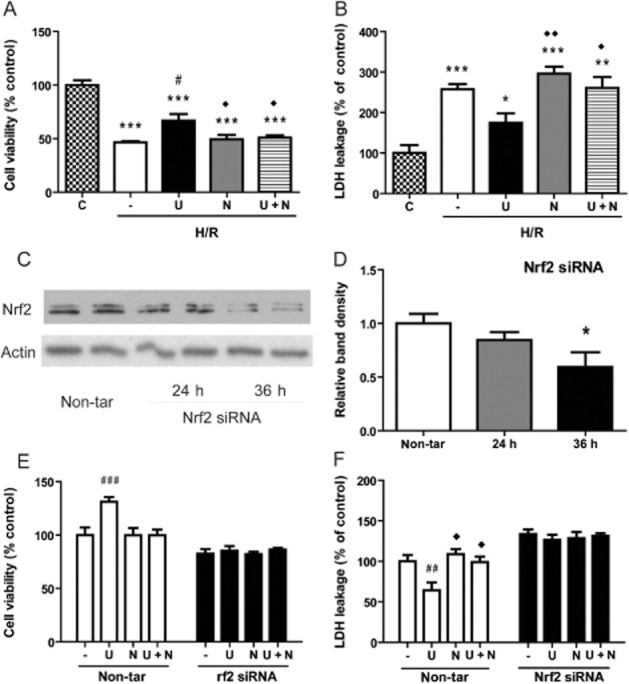
Role of Nrf2 in DOR-mediated protection against H/R injury. In (A), cell viability (with MTS) and, in (B), cell damage (LDH leakage) were measured under different conditions: vehicle treatment in normoxia (C) and after H/R (0.5% O2 for 16h followed by 21% O2 for 4h) vehicle (−), UFP-512 (U), naltrindole (N), or UFP-512 plus naltrindole (U + N) exposure. In (C) and (D), HEK293t cells were transfected with Nrf2 siRNA and assayed for Nrf2 content 24 or 36h later, in normoxia. In (E ) and (F), cells were transfected with Nrf2 or non-target (non-tar) siRNA and exposed to H/R, without further treatment or incubation with UFP-512 (U), naltrindole (N), or UFP-512 plus naltrindole (U + N). In (E), results from assays of cell viability and, in (F), of LDH leakage are compared with those of the control cells transfected with non-target siRNA. Data shown are means ± SEM of three independent experiments. —, H/R alone. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, significantly different from control (the non-treated) cells in normoxia; # P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.005, significantly different from non-treated cells after H/R stress. ◊P < 0.05, significantly different from UFP-512 after H/R stress. n = 4 per group. Note that H/R decreased cell viability and increased LDH leakage, effects attenuated by UFP-512 (A and B). Co-treatment with naltrindole abolished the UFP-512-induced protection. After Nrf2 siRNA transfection, Nrf2 protein was knocked down (C and D) and DOR activation with UFP-512 no longer induced any protective effect on the cells. In the control cells with non-target siRNA transfection, however, treatment with UFP-512 was still cytoprotective (E and F).
