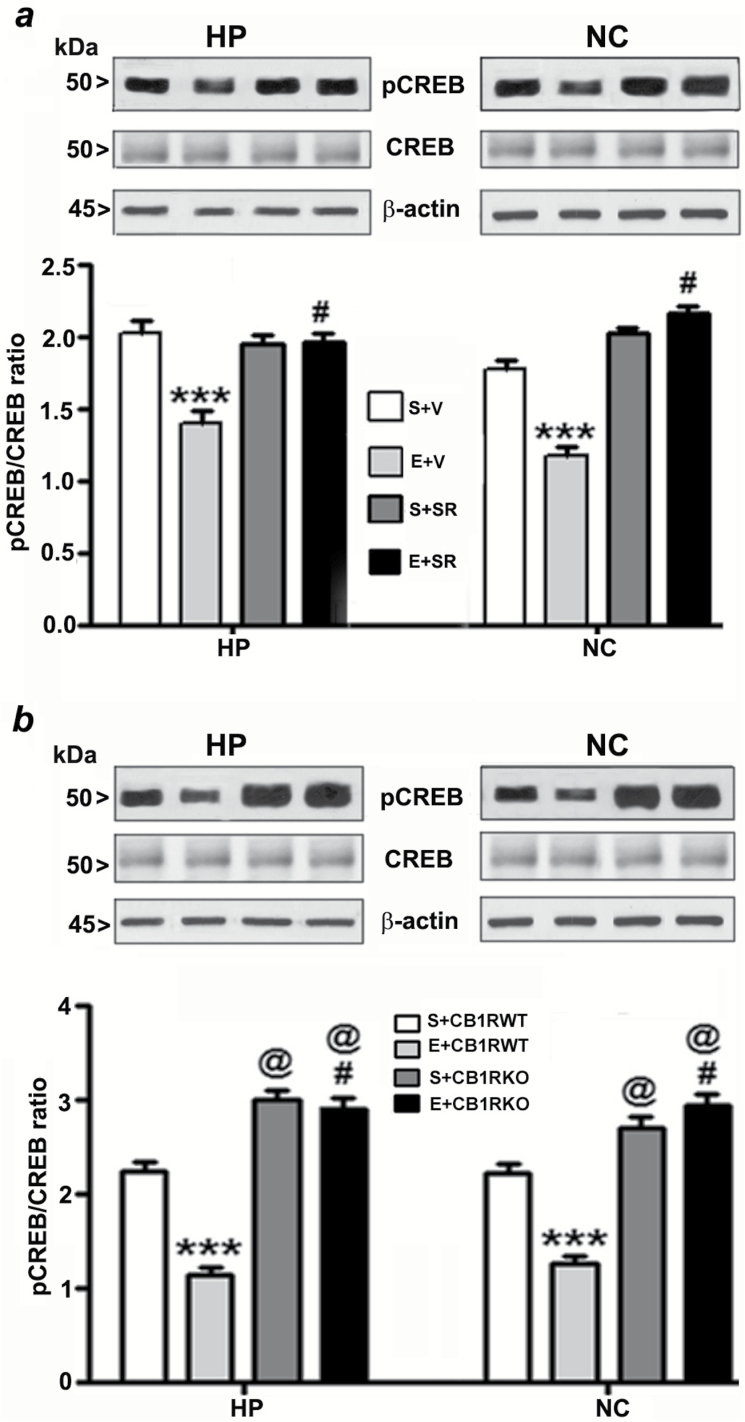
Figure 3.
Pharmacological blockade or genetic ablation of CB1Rs provides protection against ethanol-induced inhibition of CREB phosphorylation in the neonatal mouse brain. (a) Hippocampal and neocortical nuclear extracts from the four treatment groups (S+V, E+V, S+SR, and E+ SR) were subjected to Western blot to analyze the levels of pCREB and CREB (n = 10 pups/group; ***p < 0.001 vs. S+V; #p < 0.001 vs. E+V). (b) Additional Western blot analyses were performed to determine the levels of pCREB and CREB in the hippocampal and cortical nuclear extracts obtained from the saline and ethanol-treated P7 CB1RWT and KO mice. The representative blots are shown for the hippocampal and cortical nuclear extracts (n = 10 pups/group; ***p < 0.001 vs. S+CB1RWT; #p < 0.001 vs. E+ CB1RWT; @p < 0.001 vs. S+CB1RWT). β-actin was used as a loading control. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc tests was used for statistical analysis. Each point is the mean ± SEM. HP, hippocampus; NC, neocortex.