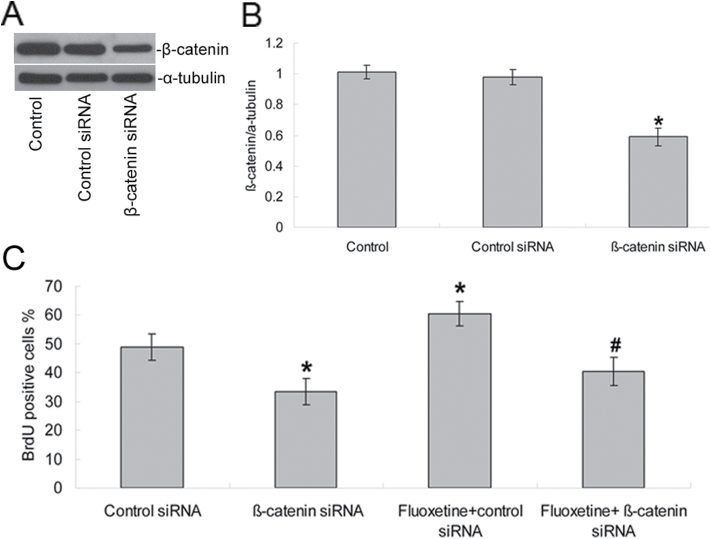
Figure 6.
Inhibition of β-catenin expression decreased NPC proliferation and reduced the proliferative effects induced by fluoxetine. NPCs were transfected with β-catenin siRNA or a fluorescein-conjugated control siRNA. (A) β-catenin protein expression was detected by Western blotting and indicated a decrease expression (B). Values represent means ± SD (n = 5). *p < 0.01 versus control siRNA group. (C) 48h after transfection, some of the cells (as noted) were treated with 1 μM fluoxetine for an additional 48h before their cell proliferation was measured by BrdU labeling. Analyses of variance revealed main effects for β-catenin siRNA and fluoxetine treatment on NPC proliferation [F (1, 18) = 75.13, p < 0.0001 for β-catenin siRNA; F (1, 18) = 20.74, p < 0.0001 for fluoxetine]. Values represent means ± SD (n = 5). *p < 0.01 versus control siRNA group; #p < 0.001 versus fluoxetine + control siRNA group. BrdU, 2 d, 5’-bromo-2-deoxy-uridine; NPCs, neural precursor cells; SD, standard deviation; siRNA,.